Insulation at home is critical. A vital factor to consider when choosing insulation is the R-value. You need to select the right materials that will help you regulate indoor temperatures. The R-values will vary on the materials, existing structures, and requirements. In this post, you will know if R-values add to insulation abilities.
The R-values are additives for the layers of insulating materials. The materials should be dense solids with direct contact with insulated surfaces. Yet, the thermal resistance level depends on the material's composition and thickness. The R-values increase when you add more layers of heat-resisting material.
The R-value is important to consider because it is the measure of an insulation's capacity to resist heat flow. You can get better insulation if you know how to choose materials that add to the R-value. Continue reading to learn how R-values add to insulation.

Why Is R-Value An Additive?
The R-value is the ability of insulating materials to resist heat flow. It is also a measurement of the energy-saving capabilities of insulation.
R-values will add up to get the total thermal resistance of insulation materials. If you add a material with an R-value of 5 to existing insulation with an R-value of 13, the total value will be 18. You get higher R-values if you add more materials with insulating properties. The values will vary based on the composition and location of the materials in the house.
Moreover, doubling the thickness of the materials will double the R-values. In effect, the insulation cuts the heat loss in half.
If you want better insulation, select the materials with high R-values.
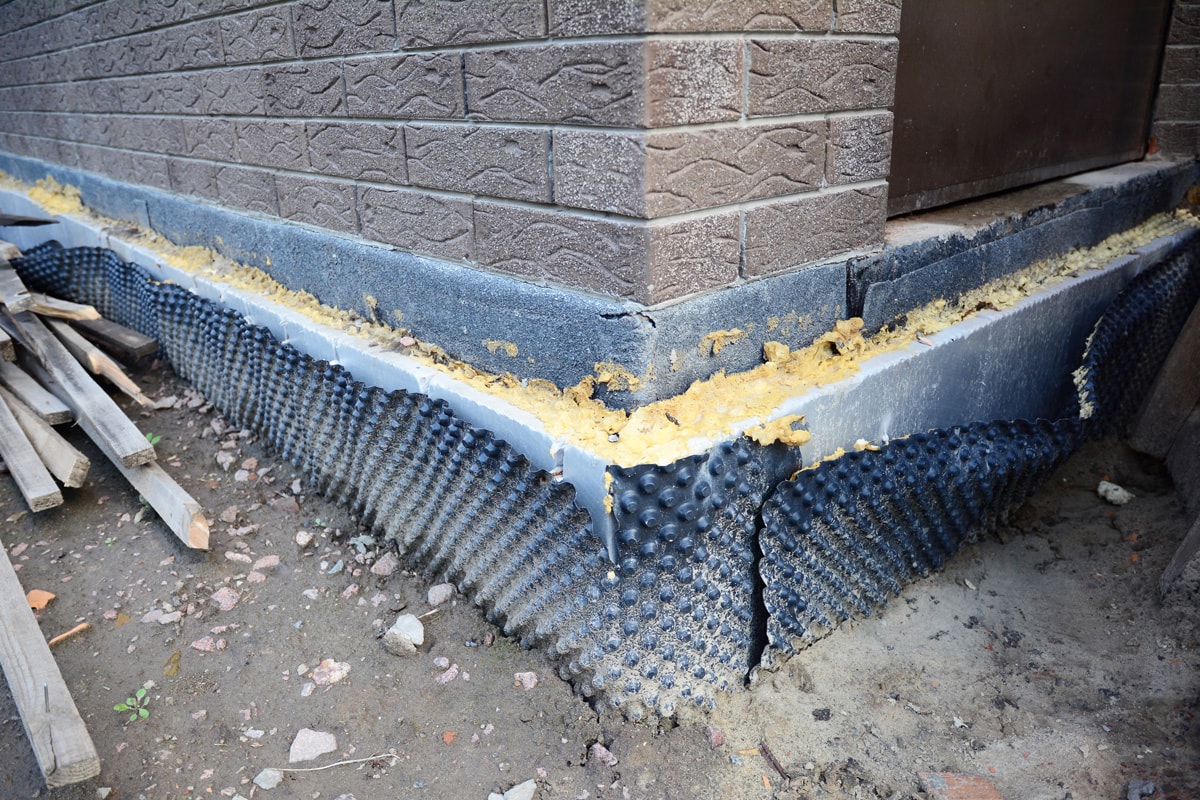

What Materials At Home Have R-Values?
The insulation materials have varying R-values for different applications. Here is a list of materials used for insulation:
- Blanket (batts or rolls)
- Concrete block
- Foam board/rigid foam
- Fiber insulation
- Insulating concrete forms
- Sprayed foam
- Structural insulated panels
Besides insulating materials, common building materials have inherent R-values. The values are not as high as insulation, but you can consider the values if you will add a layer of insulation. Listed below are the typical materials:
- Air films
- Building sheets (e.g., plywood, chipboard, plaster)
- Bricks and concrete
- Glass
- Tiles
- Carpet
The materials with low R-values have less resistance to heat because of their convection, conduction, and radiation properties. They will not be as effective as rated insulation materials with specialized compositions. The materials with higher R-values are very dense or solid to resist heat transfer.
Check here for the R-values of different home materials.
Does Higher R-Value Mean A Better Insulation?
A Home R-values matter since it helps with energy conservation. A higher R-value means that it has a better insulating capability and thermal break. The insulation works hard to minimize heat loss. Your home can keep warm during the cold season and cool in the summer. As a result, you get lower electrical bills.
A home without insulation will require air conditioners and HVAC systems. Using the machines will need electrical power. Yet, electricity is not free. So, every usage will increase your utility bills. Also, you don't strain the machines too much if you have the right R-values for your home.
Here are other benefits of using materials with high R-values:
- Comfort at home
- Sound dampening
- More environment-conscious
- Added resale value
Yet, you can only benefit from higher R-values with a quality installation. The real R-value can be more or less 1/3 of the original value. So, you need to know the suitable R-values to add to your home.
What R-Values Do You Need At Home?
There are areas in your home that will need a minimum R-value. Some parts of a house will need more heat resistance due to the purpose or location. The typical recommendations are the following:
- Exterior walls: R13-23
- Ceilings and attics: R30, 38, 49
- 2x4 walls: R13-15
- 2x6 walls: R19-21
- Floors and crawl spaces: R25-30
You also need to consider the climate zone of your house when selecting materials. There are 8 US climate zones, each with different heat levels and insulation concerns.
In addition, the cooling and heating systems influence the R-value needs of your home. If you need to reduce heat loss, you must use the machines often. You can get support from R-value-rated materials for efficient use of energy.
In addition, you can get the overall heat transfer of the composite materials by converting the R-value to U-value.
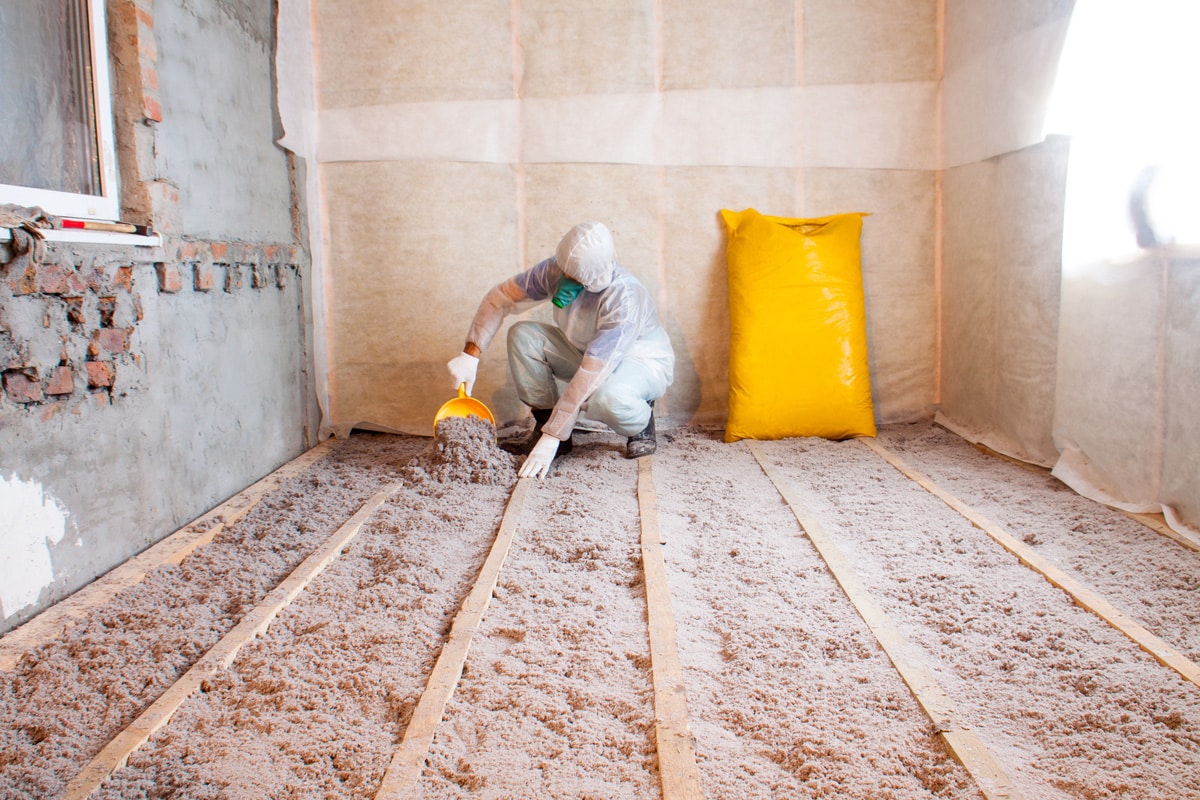

How Much Difference Does R-value Make?
Adding materials with R-values ranging from 1-30 can reduce heat loss by around 3%. If you add the materials, ensure the proper installation because the R-value additive can reduce the total value. If you want a higher percentage of heat loss, you should ensure the correct installation of the materials.
Learn how to compute the heat loss from Indeeco.
Can There Be Too Much R-Value?
It is beneficial to add more high R-value materials. In the usual course, increasing the R-value will reduce heat flow. You can add the same or different R-values to get more heat resistance. However, there is a limit to everything too much. Adding more layers of insulation has diminishing returns.
A study from Energy Vanguard shows that there is a decreasing effectivity when you add more R-values.
Their data shows that adding insulation to uninsulated homes is more energy efficient than previously insulated homes. When constructing your home, you should start on the minimum required R-value of the space. Adding smaller R-values will only result in smaller gains because you start from small heat losses.
Conversely, adding choosing very high R-values does not guarantee more energy efficiency. There can be errors in installation, or the climate zone does not require a high R-value material. You must consider several things before adding R-values.
Here are the following factors affecting R-value limitations:
- Climate zone
- Comfort
- Heating and cooling systems
- Household goals and needs
- Installation technique
- Material
- Local code requirements
- Utility costs
Does Stacking Insulation Increase R-Value?
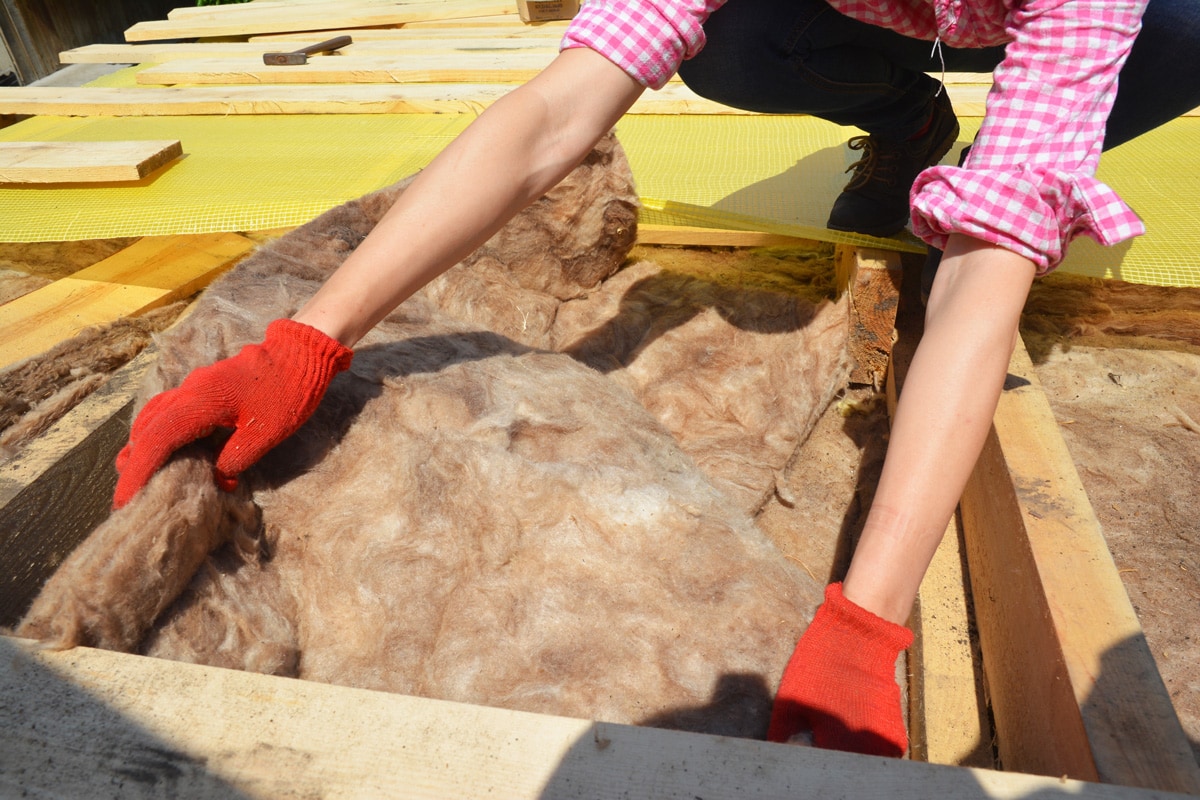

Yes, stacking will increase R-value. Just add the values of the materials to get the total R-value. If you have a layer of loose-fill insulation, you can add it with batts. Another example is mixing rolled fiberglass with blown-in insulation. The materials you stack are compatible and suitable for your needs.
Read from this post if Can You Mix Different Types Of Insulation? [Esp. Blown-In].
However, there is a downside if you stack insulation. If you put too many layers, the insulation can compress. As a result, the insulation R-values reduce, and you will not benefit from insulation. Compression can happen if you add dense insulation over a lighter one. You only add an inch over existing fiberglass insulation or half an inch for cellulose or rock wool.
When stacking over existing insulation, you should not stack on a deteriorated or damp material. The benefits of stacking are useless if you don't keep all layers in good condition.
Can You Stack Rigid Foam Insulation To Increase R-Value?
Yes, you can stack rigid foam insulation to increase energy efficiency. The R-value of rigid foam is around 3.6-8 per inch of insulation. If you increase the strength of this insulation, it will handle more heat.
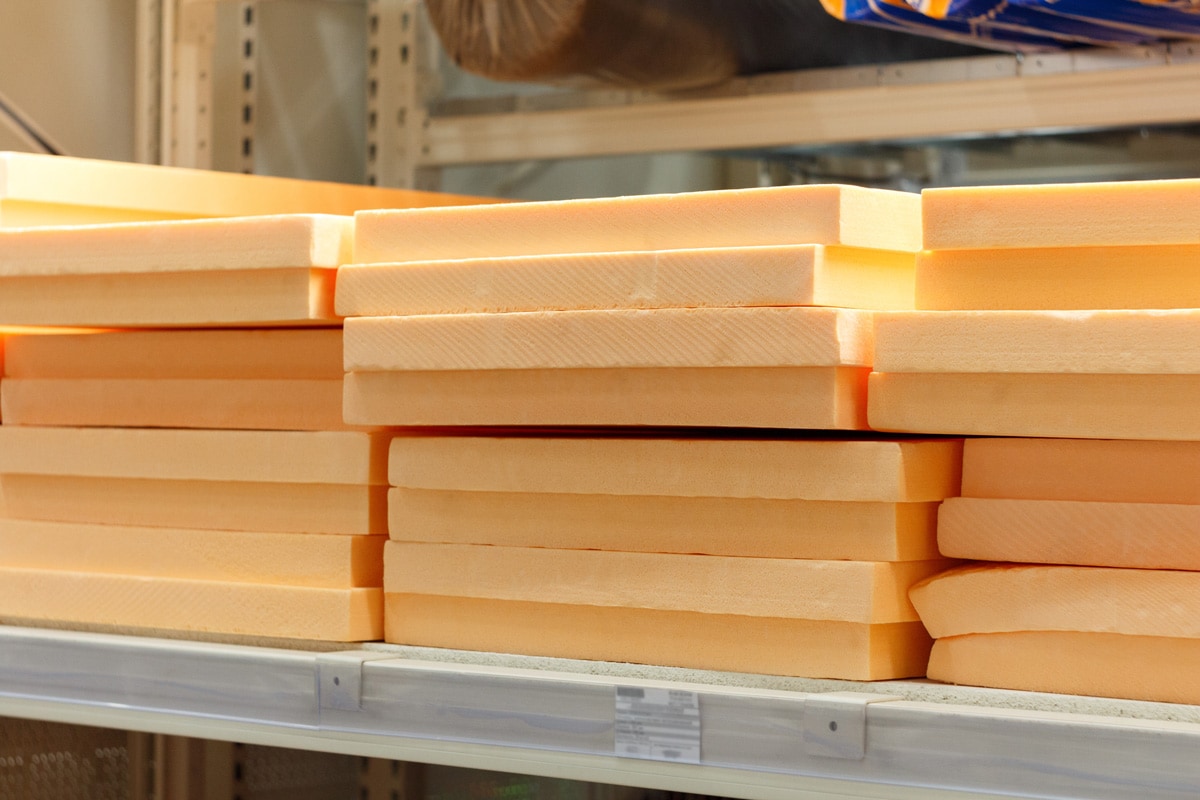

The R-value of polyurethane spray foam is the least, while the highest is polyisocyanurate. Other than the R-value, you should consider the climate zones and your home's needs before selecting what type of foam insulation to stack. Expanded polystyrene is inexpensive, and most homeowners choose this to achieve a higher R-value.
In Closing
R-values are additives to existing insulating materials. If you add higher R-values materials, the total R-value of the insulation assembly increases. You can combine other insulating and common construction materials to get a high R-value. However, the R-value's strength can diminish if you add more layers over time.
Consider your climate zone and needs if you want to get better insulation. Finding the right materials with suitable R-values will make a difference. You get more energy savings and better temperature control with suitable R-values.
If you are adding on top of existing insulation, you should remember not to compress old and new materials. If you do, the R-value decreases, and the energy efficiency decreases. Hence, it would be best if you were careful when installing the materials.
After all, R-values will help you achieve a more comfortable home.
Learn more about R-values from these posts: