As with anything else, your hands, eyes, and hearing are the best initial diagnosing instruments. It's crucial to emphasize that charging and checking the refrigerant charge are two distinct processes that can be carried out without gauges. We've done the research and come up with concrete responses to your inquiries.
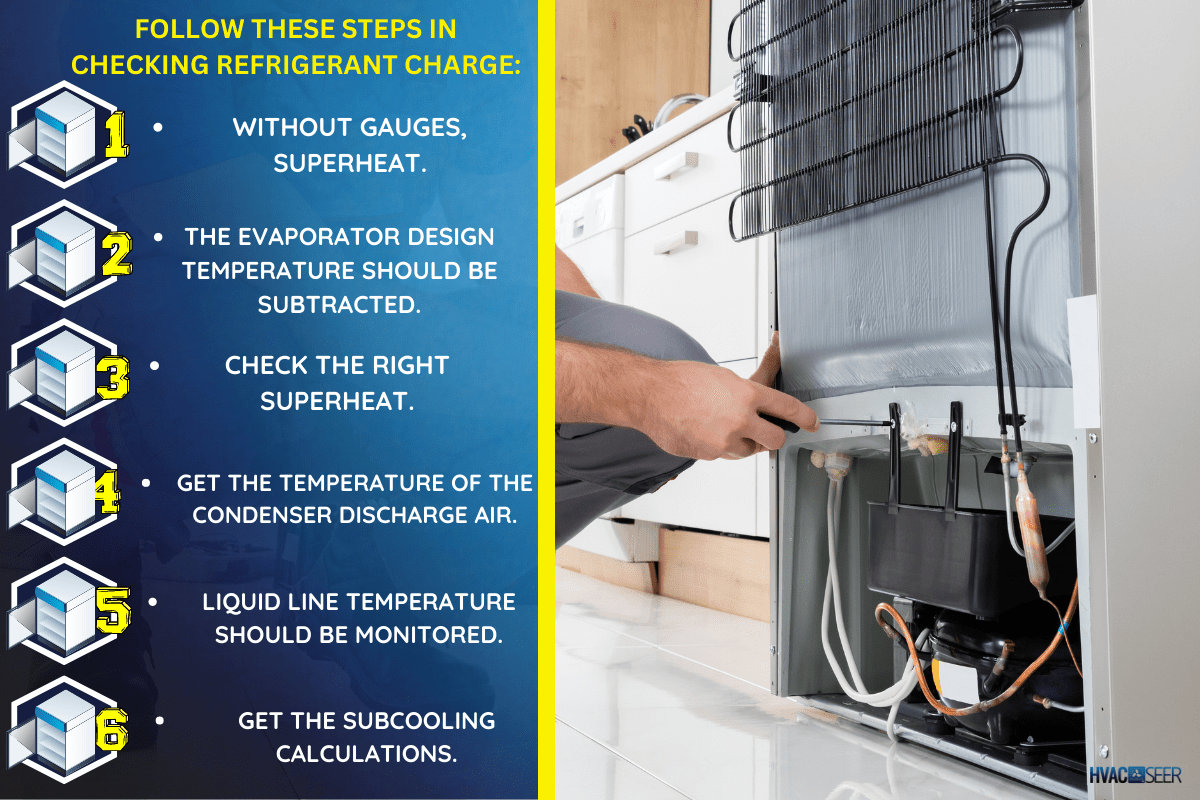
Follow these steps in checking refrigerant charge:
- Without Gauges, Superheat.
- The evaporator design temperature should be subtracted.
- Check the right superheat.
- Get the temperature of the condenser discharge air.
- Liquid line temperature should be monitored.
- Get the subcooling calculations.
Since the refrigerant circuit is sealed, adding piercing valves and "invading" it to test it would be the last thing you would do if it had a problem. Continue reading because we have extensive research on this subject and have lots of valuable data to share.
Refrigerant
There are various kinds of refrigerants, and they are categorized according to their chemical composition and ability to deplete the ozone layer. You might also want to review the fundamentals of what influences the pressures inside the system and what results in the various modifications and conditions of the refrigerant. The procedures for checking refrigerant without gauges are as follows.
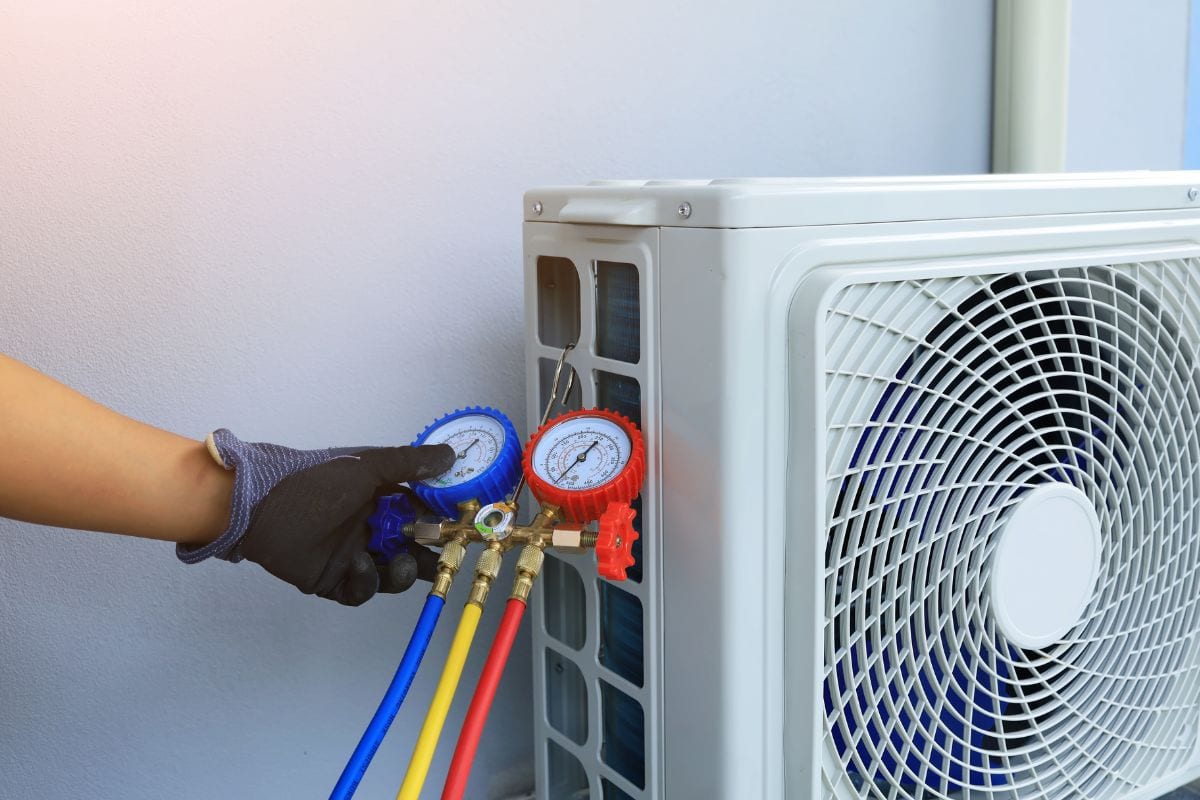

Superheat
We must first identify what should be our superheat. The interior wet bulb measured in the return air and the outdoor dry bulb measured in the shade near the condenser are required to use the system's superheat charging chart.
Evaporator Design Temperature
The return air dry bulb is subtracted from the evaporator design temperature differential. The difference between the return air temperature and the evaporator saturation point, which you can see on the lower side of your refrigerator gauges, is the evaporator design temperature.
The saturation temperature of the low side of the system is essentially obtained by deducting the evaporator design temperature difference.
Confirm Proper Superheat
For the most precise temperature, measure the suction line output temperature as closely as possible to the evaporator.
Temperature
The condenser discharge air temperature will determine the saturation temperature of the refrigerant in the condenser. The pressure-temperature relationship can be applied to convert the saturation temperature to the refrigerant gauge pressure using a refrigerant slider.
Measure the temperature of the air leaving the condenser in a few different locations. In most cases, the greatest number obtained after a few tries is used.
Liquid Line Temperature
Cover the temperature probe to prevent misleading readings from being caused by direct sunlight. From the liquid line service valve, note the temperature of the liquid line.

Calculate Subcooling
The formula for calculating subcool is the condenser saturation temperature subtracted by the liquid line temperature.
How Can I Tell If The Refrigerant In My AC Is Running Low?
When a system is low on refrigerant, how can you tell? You'll probably pay a higher electric bill than usual, and you run the chance of an expensive air conditioner malfunctioning. We conducted the study for your convenience, so you can stop wondering.
Consider these five warnings of low refrigerant:
- It takes a lot longer to chill your house than it should.
- You have higher-than-normal utility bills.
- Your vents aren't blowing out cold air.
- Ice is beginning to accumulate on your refrigerant line.
- Your unit is making loud or strange noises.
Don't let hot temperatures and high energy expenses from low refrigerant mar your summer. Service your air conditioner right away to restore both your home's temperature and your electric bill to normal. For more fascinating details, keep reading.
Air Conditioner Is Losing Refrigerant
Your AC system's refrigerant is its life force, so if you don't have the correct quantity, it won't be able to cool your house adequately.
However, figuring out whether or not your AC system requires refrigerant can be challenging because low refrigerant symptoms can also be signs of other problems with your AC.
Let's discuss the warning signals that your air conditioner is losing refrigerant.

Longer Than Usual
Have you recently noticed that it takes longer to cool your house? You might not have enough freon. Keep in mind that the purpose of the refrigerant Freon is to remove heat from the air.

The air conditioner won't operate effectively if there isn't enough freon in it. Your air conditioner works overtime to cool your house when the weather is high. Low refrigerant, high indoor temperatures, and high prices make this worse.
High Utility Bills
You can find problems with your HVAC system by comparing your utility bills from month to month and from year to year. Have your air conditioner serviced if your electricity bills are higher than usual.

Your air conditioner will need to run longer and harder to cool your house if it is short on refrigerant. An increase in electricity costs may result from all the extra energy required to complete this additional work.
Cold Air
The air from an air conditioner won't be as chilly as it should be when the Freon level is low. It might even be warm or lukewarm. Check the air coming from the vent's temperature using a thermometer.
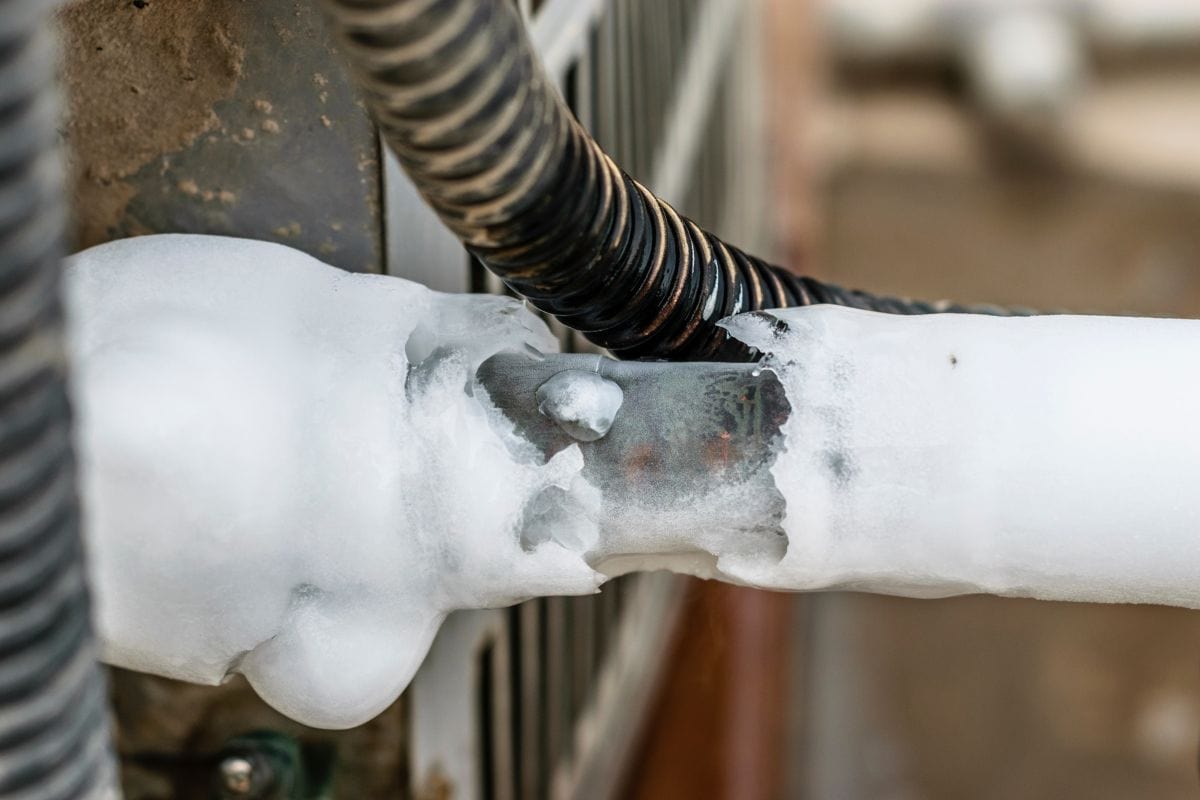
Ice
Check the unit for ice buildup if you think your air conditioner's refrigerant levels are low. When an air conditioner lacks refrigerant, ice can build up on copper tubing or the evaporator coil.
The evaporator coil gets considerably colder than it should when there isn't enough refrigerant in the system, which causes the moisture on its line to freeze up.
Loud Strange Noises
Unlike gas, which depletes over time, refrigerant does not. When there is a leak, units often start to run out of refrigerant. A hissing or bubbling sound could result from an AC refrigerant leak that must be fixed.
How Can I Tell If My AC Is Overcharged With Refrigerant?
The compressor is at the most danger from the overcharged refrigerant. The compressor may permanently malfunction if there is too much refrigerant present. To assist you, we conducted in-depth research on this subject.
These are the signs of having an AC that is overcharged with refrigerant:
- Layers of Frost
- Higher Heat Discharge
- Loud Screeching Sounds
- Uneven Pressure Levels
- Very High Energy Usage
- Extreme Cold
- Erratic Behavior
As a homeowner, you could experience various AC issues due to a refrigerant problem. Experts advise homeowners to have the unit refilled whenever they are coping with one of these problems. For more details, keep reading

Layers of Frost
Frost is typically difficult because it could have two very different sources. Low refrigerant levels can produce a frozen condenser occasionally, although an overcharged system can also cause it.
If you observe these symptoms, contact a professional to examine your AC to be certain.

Higher Heat Discharge
If really hot air is being expelled from the vents, the system may be producing more heat inside the appliance. Overloaded condensing lines and overworked motors are often the blame for this.
In addition, you might have an overfilled system if you observe a rise in heat discharge following a recent maintenance check that included refrigerant charging.
Loud Screeching Sounds
Loud screeching sounds from the compressor can be related to the air conditioner's lines being under pressure. A liquid called refrigerant is sprayed through the compressor as a gas.
The chemical, still in liquid form, is forced through small nozzles and spray hoses when too much of it is pumped into the pressured lines.
This causes squealing sounds, which may seriously harm the moving elements of your air conditioner.
Uneven Pressure Levels
If you don't have the necessary testing tools, it is recommended to have a professional conduct AC pressure tests to check for uneven pressure levels. It would also be safer to call an expert rather than try to solve any problems alone.
Very High Energy Usage
One of the most apparent indicators to ever appear might be this one. The cooling cycle will be thrown out of synchronization by the higher pressure caused by more refrigerant, putting more strain on the air conditioning system. There will be a rapid increase in energy use as a result.
Extreme Cold
Air conditioners aren't made to withstand sub-zero temperatures, according to experts, who claim that extra refrigerant in an overcharged residential or commercial AC unit will collect inside the compressor.
This can lead to serious and pervasive faults, coupled with the danger of extra refrigerant seeping into the electronics.
Erratic Behavior
It is anticipated that the strain brought on by too much refrigerant may produce erratic shutdowns, as well as squealing sounds originating from the outdoor unit and warm air entering the house through the vents.

A complete shutdown may occur if your AC is overloaded and the compressors are burned out. In this situation, you won't be able to turn your air conditioner back on until a professional has serviced it.
In Closing:
Superheat, and subcool measurements are crucial for determining a system's refrigerant charge.
You can check the refrigerant charge without gauges by following six easy steps because your hands, eyes, and hearing are your best initial diagnostic instruments.
Gauges are only connected when necessary or when there is a reason to do so.
For more related information, check out these articles: