Airflow configuration is important when choosing the right furnace for your home's HVAC system. But how would you know which furnace airflow configuration is suitable for your home? We asked the experts about it and here's their answer.
Airflow configuration refers to where cold air enters and warm air leaves your furnace. Upflow furnaces are recommended for those with basements. Those who don't have basements can have downflow furnaces installed in their attic. Meanwhile, those with low ceilings can have a horizontal furnace installed in their homes.
Keep on reading to know more about these furnace airflow configurations so that you can understand which one will suit your home best. We'll also tell you the importance of good airflow and guide you in choosing the best furnace for your home. Let's get down to business!
![Types of furnances that is compatible for your type of home, Downflow Vs. Upflow Vs. Horizontal Vs. Counterflow Furnaces [Which Configuration Is Right For Your Home?]](https://hvacseer.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/1.png)
What is the difference between upflow, downflow, horizontal, and counterflow furnaces?
A furnace keeps your house warm even on the coldest winter night. It does so by pushing heated air out of the ducts and pulling cold air into its system to be converted into warm air, and the cycle continues.
Furnaces follow a systematic way of converting cool air to heated air and distributing it to your ductwork. Their physical orientation or design is crucial in helping them do this. It would determine where cold air enters and warm air leaves before it flows to your ducts and out of the vents.
Having the right furnace airflow configuration will determine how efficient your furnace will be in responding to your heating needs. Most furnaces are installed in the basement, but how about those who don't have a basement? The workaround here is to have a furnace with a different airflow configuration so that you can still install one to answer your home's heating needs.
Without much further ado, we'll talk about the different airflow configurations and where they could be used.
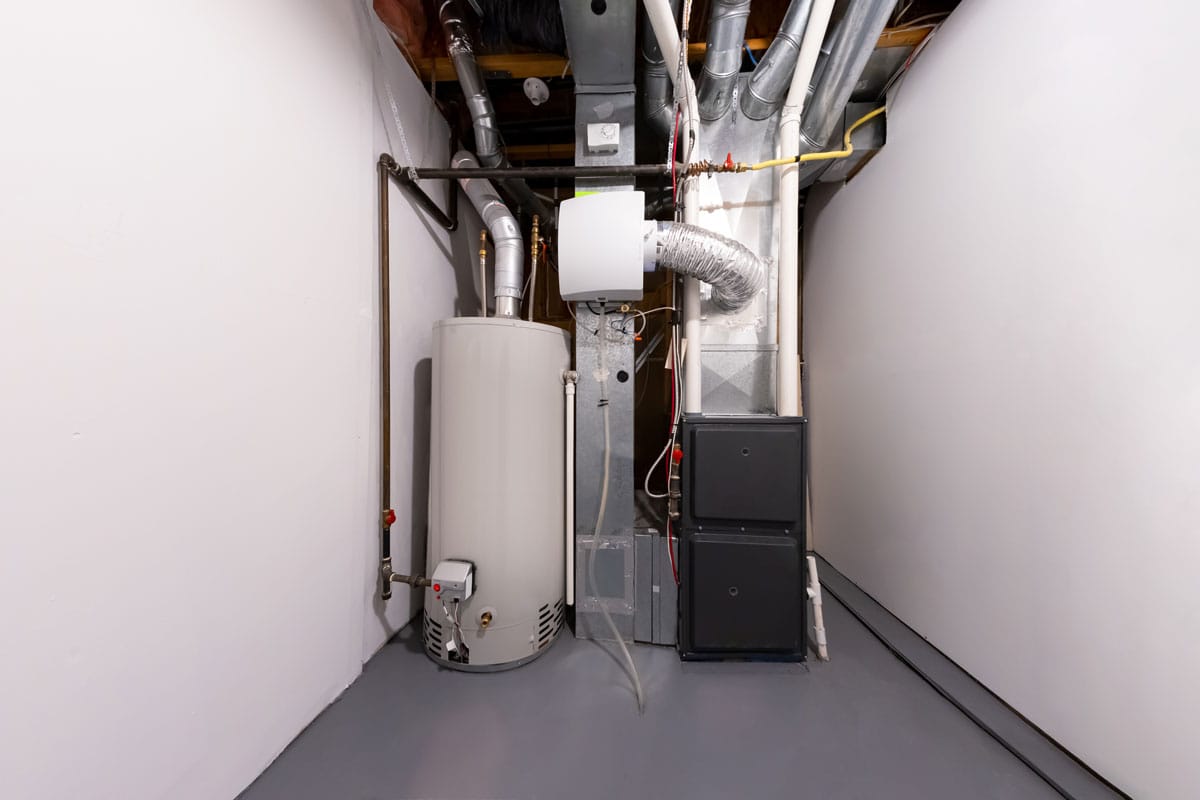

Downflow Furnaces
Downflow furnaces are also called downdraft furnaces. Cool air enters from the top of the air handler, and warm air goes out from the bottom of the furnace. The ductwork is positioned below the unit so that warm air can be distributed to different parts of the house.
They work best for homes without a basement and have a slab foundation. They can be placed in the attic and connected with the HVAC duct system. Some also have them installed in the garage or a closet on the main floor.
But remember, hot air flows upward, so this isn't really the ideal airflow configuration. However, homeowners have to make do with their specific circumstances that would require the use of this type of furnace.
This is less energy-efficient and would require some minor construction work with the attic's subflooring for reinforcement and adding a fire-resistant layer between the furnace and flooring for safety purposes.
Since hot air is coming from the attic or higher portion of the house, one's head and upper body parts are heated first. This can make some people uncomfortable.
Upflow Furnaces
Upflow furnaces are found in most homes that have space in their basements for full-sized units (a.k.a. highboys) designed with blower fans beneath the heat exchanger.
The lowboy type of this furnace is recommended for those with low ceilings and low clearance since they are smaller in size. Their blower fans have been repositioned behind or beside the heat exchanger so that they won't take up too much vertical space.
With upflow air configuration, cool air enters through the bottom or top of the air handler, and heated air is released through the top side of the furnace. It then travels through your home's ductwork to be released in different vents inside your home so that every part is supplied with warm air.
Another feature of this type of furnace is that the ductwork is located above the furnace. This follows the natural tendency of hot air to rise. This means that the heated air from the furnace needs less assistance to flow into the ducts.
There's less energy consumption which translates to reduced electric bills. Air will be coming from the floor registers. This makes it easier to spread the heat throughout the room.
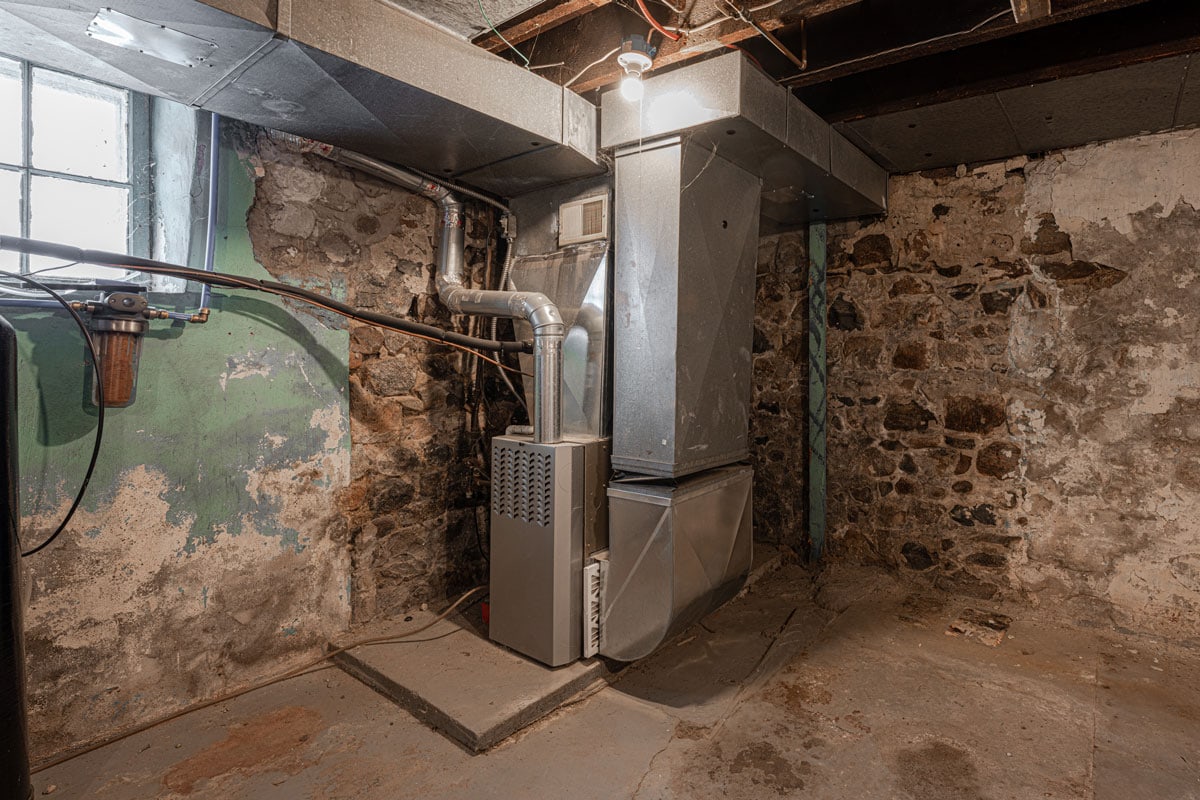

Horizontal Flow Furnaces
These furnaces look like a furnace that's lying on its side. Untreated air enters on one side, and heated air leaves from the other side. Units are referred to as the horizontal left or horizontal right furnaces pertaining to the side where warm air comes from.
These are ideal for homes with limited spaces. They can be installed in crawl spaces or basements with low ceilings.
Counterflow Furnaces

Counterflow furnaces are just the same as downflow furnaces. They take in cool air from the top and dispel heated air at the bottom of the furnace towards the ductwork that can be found underneath. These are usually installed in the attic due to a lack of space or having no basement.
In effect, there are only three main airflow configurations for furnaces - upflow, downflow or counterflow, and horizontal flow.
How do I know which furnace configuration I need?
The simple answer to this question is to have a licensed HVAC technician check your home and assess which furnace configuration will work best, given your home's layout and your heating needs.
Aside from the three furnace airflow configurations discussed above, your HVAC technician might also recommend furnaces that can be configured in different ways.
There are furnaces available in upflow/horizontal and downflow/horizontal configurations. With upflow/horizontal furnaces, installers can have the airflow configured to be either upflow or horizontal (but not downflow). Meanwhile, downflow/horizontal can be configured to go downflow or horizontal (but not upflow).
Lastly, multipositional or multi poise furnaces can be configured by your HVAC installer so that the airflow can go up, down, horizontal left, or horizontal right, depending on what will work best with your home's layout. If you're not sure about the airflow configuration that would suit your home, these furnaces offer maximum flexibility and can be adjusted according to your heating needs and available space.
Why is airflow important in HVAC?
We've been talking about the different types of airflow configurations. Now let us discuss why proper airflow is important and why you need to carefully consider this before choosing the right furnace for your home.
You will enjoy the following benefits when there's balanced airflow in your HVAC system.

Less Cost
When there's proper airflow, you can save money because your HVAC becomes more energy-efficient. It doesn't need to work so hard to provide you with a comfortable indoor temperature. It also provides your desired temperature level at a faster rate; that's why you consume less energy.
Better Indoor Air Quality
Good air circulation can help remove indoor pollutants such as bacteria, dust, and mold. It also gets rid of the musty smell in the room. You will experience fewer allergic reactions. In general, it keeps your family healthier since you breathe cleaner air.
Comfort
When the air flows smoothly, it evenly cools all rooms in your house, which means that everyone is comfortable no matter where they are in the house.
Longer Furnace Lifespan
Since your furnace doesn't have to overly exert itself to provide your desired temperature, its components won't succumb to premature deterioration. Wear and tear is inevitable, but it doesn't have to happen soon when your furnace's airflow is balanced.
To further ensure good airflow in your furnace, open all vents within the house for even heat distribution. You should also change the air filter regularly as part of its maintenance. Some filters need to be replaced faster than others. You better check the owner's manual for the manufacturer's recommendations regarding the filter change schedule.
How do you know what kind of furnace you need?
If you're still in the process of looking for the perfect furnace for your home, these are two major factors that you need to consider aside from the airflow configuration that we discussed earlier.

Fuel Source
There are four types of furnaces depending on their fuel or power source.
Gas Furnaces
These are the most common furnace types on the market. They are powered by natural gas. There are companies that supply homes with natural gas, which makes it more convenient for homeowners.
The upfront cost of these furnaces is quite expensive, but in the long run, users get to save money because their operational cost isn't that expensive. They can also heat your home faster, which means that they are more energy-efficient.
Electric Furnaces
These are powered by electricity. They are affordable, easy to install, and convenient to use. However, these furnaces are expensive to operate since they run on electric power.
This type of furnace is recommended for places that have warm or milder climates where little heat is needed throughout the year.
Oil Furnaces
These furnaces use home heating oil. The oil tank is usually buried near the home. They are also energy-efficient since oil produces a hotter temperature when burned.
Propane Furnaces
They require the use of a propane tank. These are easy enough to install. They can heat your homes more efficiently and don't consume too much propane gas when heating your home. The downside is you need to keep refilling your propane tank to have a continuous power supply.
Heat Stage
Furnaces offer different heating stages.
Single Heat
This is common among older models. These furnaces have one flame setting, meaning the heat flame size is the same throughout. They only have an on or off function, so would likely turn on and off frequently within the day, depending on the prevailing temperature.
These furnaces are more affordable, but their thermostat can be somewhat unreliable. These are recommended for smaller homes.
Multistage Heat
These furnaces offer more accurate heating. They have two sizes of flames. You can use the smaller flame for milder weather and the bigger flame when the temperature gets really cold. These furnaces are best used in medium-sized homes.
Modulating Heat
These furnaces give you more control over the flame size that you need to provide your desired temperature and maintain it at that level throughout the day. Furnaces with modulating heat are the most expensive type on the market. It is recommended for bigger homes with multiple floors.
When choosing a furnace, take into consideration its fuel source and heat stage so that you will know which one can respond to your heating needs.
Final Thoughts
Consult an HVAC professional to determine which airflow configuration is suited for your home's layout and see how your heating needs will be provided efficiently.
For more resources about your home furnace, you may visit the following posts:
Does A New Furnace Come With A Coil?
Why Is My Furnace Heating Past Set Temperature?