Heat pumps are great for maintaining temperature in the comfort of your home. They are not only purchased because of their heat-transferring system but also because of their affordability. But, if you notice that your heat pump is not as efficient in colder temperatures, you may wonder why. Is this normal, or should this be worrying? The answer is just right ahead, so keep reading to learn more.
Temperature affects heat pump efficiency, so there is nothing unusual if your heat pump does not expel much heat in freezing temperatures. Higher temperature means higher efficiency for heat pumps, while lower temperature means lower efficiency. This appliance works best at 40°F above, but when this temperature drops to 30°F below, they lose some of its efficiency.
Heat pumps and temperature have a unique relationship as the latter influences the product's efficiency. That is why you should understand how their relationship works. To do so, you must learn how heat pumps operate. For this, search no more because we have done all the necessary information-gathering for you!
How Heat Pump Efficiency and Temperature Are Related
A heat pump can both cool or warm a house depending on which mode you need it to be. Heat pumps transfer thermal energy from one place [the source] to another [the sink]. That is why its source's temperature is highly important for its efficiency.
During cooling mode, a heat pump transfers the heat inside your house or your room and expels it outside. Then, this reduces the source's heat, causing your home to cool during this mode. On the other hand, in its heating mode, this simple process reverses. The heat pump then absorbs heat outside and transfers it to your house.
This process makes the heat pump versatile for both summer and winter. It also makes them eco-friendly as they do not burn fuel to change the temperature inside a specific space. However, it means they depend on their source's temperature too.
Even when heat pumps can still transfer heat from a freezing temperature to another area, their efficiency reduces as it is much harder for them to extract heat. They work best at temperatures above 40°F, and although it works at 30°F to 25°F or below, it is not as efficient.
They also consume more energy to transfer heat at a lower temperature because it is much harder to absorb heat energy from its source.
Different types of heat pumps exist, classified according to their heat energy sources. To understand how temperature affects its efficiency depending on which heat source it is dependent on, here are three main types of heat pumps:

Air to Air Heat Pump
Air source heat pumps get thermal energy from their source's air. For cooling mode, it absorbs the heat energy from the atmosphere of your house. In heating mode, it extracts heat energy from the outside air for your home. Its efficiency then also reduces when this air temperature is low. They are much more effective if there's only minimal difference between the outside and the inside temperature. Though they can still absorb as much heat as possible, it is less efficient than when the air temperature is moderate to high.
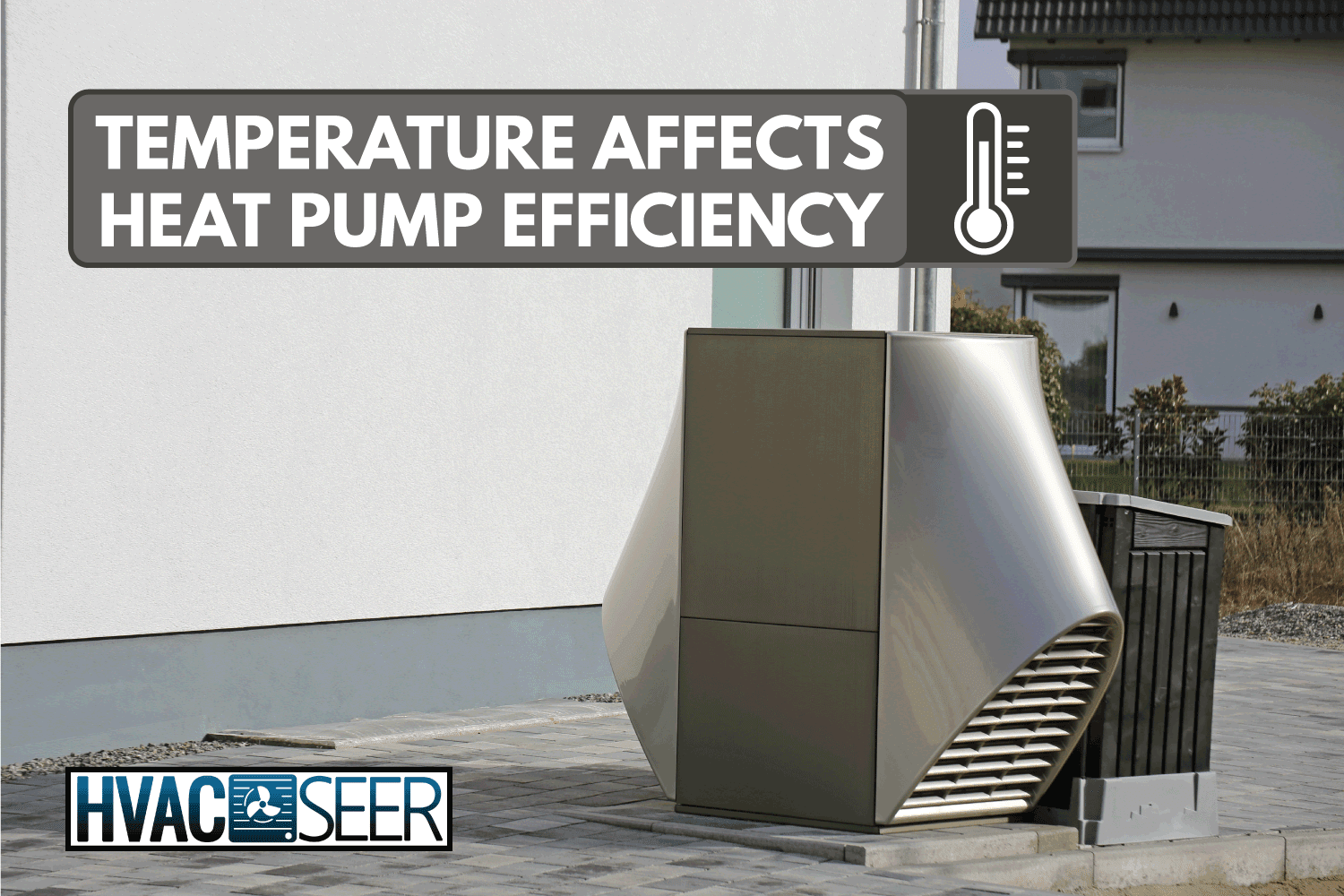
Geothermal Heat Pump
Geothermal heat pumps [ground source heat pumps] can either extract heat from the ground or release heat into it. The thermal energy from the ground is more consistent even during winter than the temperature in the air. Ground temperatures are generally 55°F or closer and do not change throughout the year, so a geothermal heat pump's efficiency does not fluctuate as much as air source heat pumps.
Water Source Heat Pump
Water source heat pumps work similarly to air or ground source heat pumps, except that their supply of thermal energy comes from the water. A large body of water such as a river or a lake should be near where you want to install these heat pumps.
They extract heat from water by cycling their pipes and then releasing the gathered energy to your house. This process then reverses in summer. Water source heat pumps rely on the temperature of a body of water which may get colder during winter, reducing their efficiency for heating. That is why they are more efficient for cooling than heating.
Best Alternative Heat Sources to Heat Pumps
Heat pumps cost you less in electricity, but because their efficiency reduces in lower temperatures, you may want to have a secondary heat source. You may need a backup heat source if you live in areas that get extra cold during winter. For this, we have browsed the net you. Here are some of the heating alternatives for you:
Furnace
They generate heat by burning propane or natural gas and then distributing the heat through their duct system. Unlike heat pumps, they do not absorb heat but produce them, so the temperature does not affect their efficiency.
Click here to see this wall furnace on Amazon.
Boiler
They heat water in their tank and then distribute the heat by pumping it to their pipes. A boiler can use oil, gas, or electricity to produce heat. This heat is used for the water or steam inside the boiler's tank to spread to warm up our home. When this water cools down, it goes back to the boiler's tank and reheats, then the cycle continues.
Check out this gas boiler on Amazon.
Pellet stoves
Small pellet stoves can heat a small room, while large pellet stoves can warm a whole house. They burn pellets made of wood or other organic-made pellets to do this. They work similarly with fireplaces but use a thermostat to increase a space's temperature. They are not just 70% to 83% efficient but also only produce small amounts of ash to clean after use.
Click here to see this pellet stove on Amazon.
Does A Heat Pump Switch to Emergency Heat?
Emergency heat is a backup heating system that provides warmth by using electricity to heat the coils within your heat pump. You can turn them on manually, but it is better not to because this system costs a lot of electricity when used.
Heat pumps automatically switch into emergency heat when the outside temperature is too low for them to move heat into your house. Typically, this setting turns on when the outside temperature is below 30°F, but it may also do so if the heat pump cannot supply as much heat as you set on your thermostat.
Read this post about emergency heat on heat pumps for more information:
When Does A Heat Pump Switch To Emergency Heat?

Can Heat Pump Freeze Up In Winter?
Heat pumps commonly freeze during winter. That is why there is a defrost function in case this happens. As the heat pump generates heat, the refrigerant it uses to transfer thermal energy condenses and may cause some frost to build up on its outside coils.
Do not worry about this because heat pumps automatically run their defrost function when necessary. If the defrost function does not properly run, the ice build-up may cause damage to your heat pump; when this happens, get it checked by a technician.
Check out this post about heat pumps freezing up for more information:
Heat Pump Freezing Up In Winter – What To Do?
What Is The Ideal Temperature For A Heat Pump?
It is best to set your thermostat to 68°F during winter or cold months. This temperature ensures enough warmth for your house and does not make your heat pump consume too much energy. On the other hand, how cool you want your home to be during summer depends on you. However, you should not set the temperature too high or too low, so you don't exhaust the appliance.
In Closing
The temperature of your heat pump's heat source influences its efficiency. Although it is still proven to work under low temperatures, it does not mean that its efficiency does not decrease. Knowing how heat pumps move energy from one place to another helps you understand why this happens. If you are worried about their reduced efficiency, you could buy a secondary heat source. On the other hand, heat pumps do not have any issues with cooling, so this should be the least of your concerns.
If the temperature isn't the issue why your heat pump isn't working well, make sure to check out this post about heat pump malfunctions for more information: