The thickness of your home's insulation can directly impact how cold or warm your home will be at any given time throughout the year. Proper insulation thickness and coverage can also directly affect your energy bills and can extend the lifespan of your home's HVAC system. So, how thick is R48 insulation specifically? We have researched this specific R-value, and we will answer this question for you.
Different insulation types will have different thickness levels based on their material. Here are the average R48 thickness levels of the most common types of insulation:
- Fiberglass Batts: 14 inches
- Closed Cell Spray Foam: 7-8 inches
- Open Cell Spray-Foam: 14-14.5 inches
- Rockwool Rolls/Batts: 14-14.5 inches
- Rigid Foam Board: 10 inches
Having the proper amount of insulation will benefit each area of your home where it's installed. Insulation locations include walls, attics, basements, and ceilings. R48 insulation is on the thicker side and best for colder regions. Continue reading to learn more about this type of insulation.

How Thick is R48 Insulation?
R48 insulation is one of the thickest R-values that you can choose for your project. Remember, the highest R-value overall is R-60--which means that it's pretty close. R48 insulation is commonly used in regions that are on the cold side or experience very cold winters.
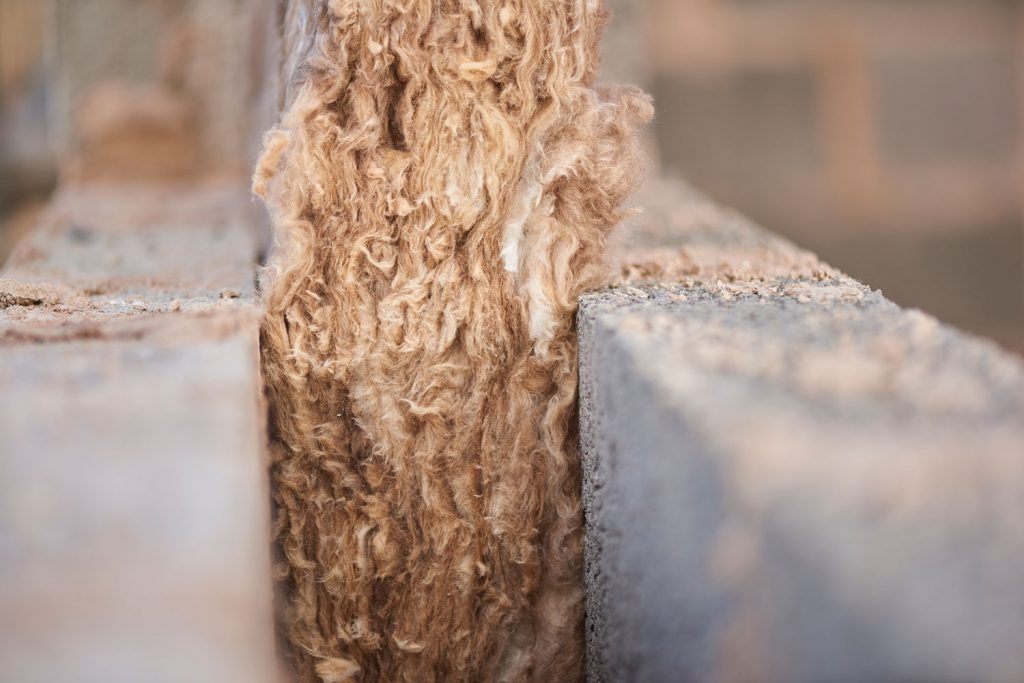

Building codes often have requirements for R48 insulation in spaces such as attics, and basements, as these areas tend to regulate temperatures the most within a home. Of course, the thickness of R 48 insulation will vary per insulation type.
How do I know how much insulation I need?
The first thing to do to determine how much insulation any room in your home needs is to check your local building codes or the Department of Energy website. You'll also want to consider the age of your home.
For example, if your home is older than 10 or 15 years, you will likely need more insulation to help regulate its interior temperatures. Note that you can also retrofit your home with mineral wool and fiberglass insulation. Once you find the recommended R-value for your area, you can search for the right material.
Each insulation material will have its characteristics, which in turn will affect how much you need for the required R-value. Let's take a closer look at each one.
Fiberglass Rolls and Batt Insulation
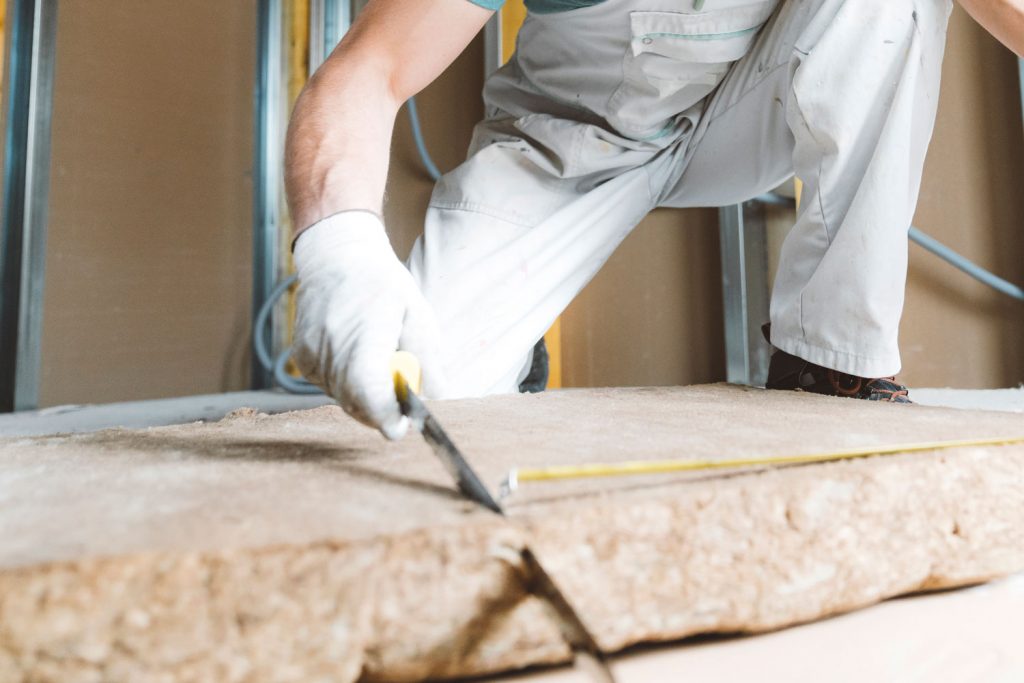

Fiberglass batts and rolls are made from thin pieces of glass and have a thick cotton-like texture. This type of insulation is usually available and widths of about 10 to 15 inches and lengths anywhere from 25 ft up to 300 ft long. Your average fiberglass insulation batt or roll will have an R-value of anywhere from 11 to 50.
Typically, these batts and rolls can be placed singularly side-by-side in the wall when it comes to wall insulation. However, to achieve an R48 insulation value, you'll likely need to double or triple the layers if installing them in your attic or basement. The total thickness may be anywhere from 2-3 feet in height.
For example, if installing it in the attic, you may need to use anywhere from two to four layers of insulation to meet your home's required R-value. Wall insulation isn't usually required to be as thick as other areas in the home.
Find fiberglass insulation on Amazon.
Rigid Foam Board Insulation
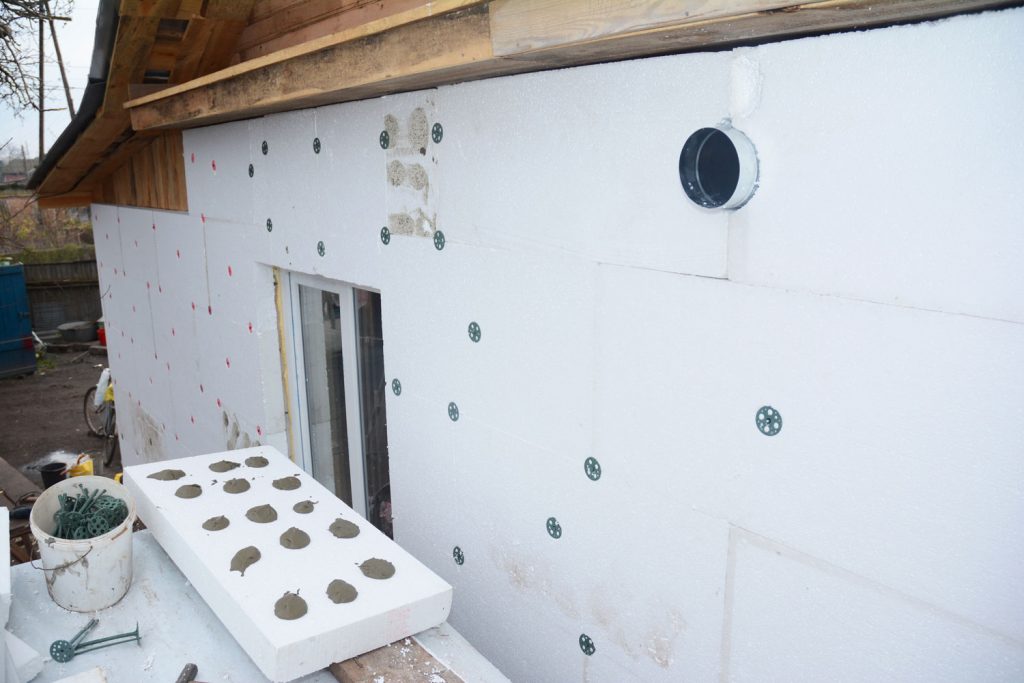

Rigid foam boards are rigid panels made from polyurethane, polyisocyanurate, or polystyrene. They can be installed in any part of your home from the basement all the way up to the roof. They are especially effective for insulating walls in the basement and upper floors.
On average, you may need anywhere from 2-5 of boards overlapping one another when installed in the walls and two or more when installing them in basement walls, ceilings, or attics. The reason is that these boards are typically no more than 2 to 3 inches thick, and their R-value will range from 5-11 per board. The total thickness of the overlapping boards may be anywhere from 10-14 inches.
You'll need to install multiple boards to meet recommended R-values for specific areas of the home [such as the attic or basement ceiling]. However, this may not always be the case, as these dense boards provide excellent thermal resistance [even up to twice as much as some other insulation materials], and they're known to last a very long time.
Loose-fill [Blow-in] Insulation

This type of insulation is usually made of cellulose, rockwool, or fiberglass. The small particles are blown into the space using a machine, so the thickness will depend on how much insulation you use. Of course, it will ultimately depend on the R-value of the specific location in your home.
For example, if you're installing R48 on your attic floor, you may need anywhere from 10 to 15 or more inches of insulation to meet this value--this layer will be fairly thick. This kind of insulation is very popular in attics, as it conforms easily into irregular shaped, small, and tight spaces.
Radiant Barrier Reflective Insulation
Radiant barrier insulation is probably the thinnest installation material available. It's designed to resist convective and conductive heat flow and helps protect from heat-producing sunlight--which is why it's commonly used on attic ceilings.
It's typically made of aluminum foil but comes with a backing made of polyethylene bubbles, plastic film, or fire-retardant cardboard. If you live in a sunny region where temperatures can soar in the summer, radiant barrier insulation can help to regulate interior temperatures during these months.
If you're using radiant barrier to meet an R48 insulation requirement, you'll need to use the type that has a fiberglass backing. This type is usually about 3-5 inches thick, so you'll need anywhere from 3-5 layers [making the total layer about 10-20 inches thick] to accommodate for an R48 value.
Learn more about radiant barrier insulation on Amazon.
What Does R-value Mean? How Is It Related to Insulation Thickness?

R-value is an industry-standard for measuring a material's thermal resistance. Essentially it is determined by the density and thickness of the insulation material. When it comes to R-value, the higher the value, the better the insulating quality of the material.
The best R-value for your home insulation will depend on where you live and the materials with which your home is made. If you're going to re-insulate your home or are in the process of adding a new room to your home, you'll need to determine the correct R-value for your region.
For example, homes located in the northeast part of the United States [the coldest part of the US] typically require attic insulation with an R-value of around 45 to 60.
While homes located in the south in the southwestern part of the United States will typically only need on average insulation with an average R-value of about 25 to 35.
To find your home's recommended R-value, you can visit the US Department of Energy's website and look up your specific geographic area. You can also consult your local building code entity or government to get this information.
What is the standard thickness of insulation?
It depends on the type of insulation to which you're referring. For example, your typical fiberglass batts and rolls can range between 2-6 inches in thickness. While the thickness of spray foam cellulose insulation will depend on how much you apply [the more applied, the thicker the insulation layer].
Rigid foam board is typically a quarter of an inch to two inches thick. Radiant barrier insulation material is relatively thin [thousandths of an inch thick] but can be 2-3 inches thick with a fiberglass or wool backing.
What is the best thickness for wall insulation?
On average, wall insulation thickness will range anywhere from 4 to 6 inches, but it will depend on your region. This is because most areas will have a recommended R-value of 13 to 16.
You can usually be accomplished this by applying one layer of fiberglass insulation are two layers of rigid foam boards. Spray foam insulation can also be used for wall interior, though the thickness level will also depend on the space between the interior and exterior walls.
It's easier, however, to install spray foam insulation into new construction than homes that are already built. This requires more time and will ultimately cost more money.
How many inches of blown insulation should be in my attic?

It depends on your region and the layout of your attic. The roofing material on your attic will also play a part in how much insulation you'll need on average.
You may need anywhere from 8 to 14 inches of insulation in your attic, with higher R-values requiring thicker coverage. This means that you'll likely need to double up fiberglass batts and rolls or rigid foam boards.
If you're using spray foam insulation, you'll want to account for the thickness needed in inches. The insulation package for the foam will list the maximum coverage, including the width, length, and depth that it can fill.
Wrapping things up

We hope this post has helped explain the average thickness of R48 insulation. Note that this insulation is on the thicker side and should be measured before it's installed in any location. Before installing new installation, always be sure to measure between the walls, floor or ceiling joists, and any cracks and crevices.
Before you go, be sure to check out our other posts: