Air ducts are one of the most vital systems in a house or commercial building. Should HVAC return ducts be insulated? So, we did some research, and here's what we discovered.
Return air ducts must be insulated if they travel through environments that affect the return air temperature. Exhaust air ducts are usually not insulated. Condensation and leaking from ducts are prevented by insulation.
The pipe network through which heated or cooled air travels in your residential forced-air HVAC system is known as ductwork. Keep reading to find out more important information about your air ducts.

Do Ducts Need To Be Insulated?
Aside from the supply ducts that deliver the conditioned air, there is also a system of return air ducts that return the exhausted air to your HVAC system. But if they are improperly sealed or insulated, you miss out on the numerous benefits of insulation.
Before supplying air through the registers, HVAC ducts travel through several rooms with varying temperatures. It implies that the system must first overcome the temperature of the duct before distributing the desired air temperature to the rest of the building.

The furnace in the basement will compel air through cold ducts before it can heat the building. The opposite occurs when you turn on the air conditioner during a hot day. Before it can effectively cool the building, it must contend with warm ducts.
Heat transfer occurs eventually and is a common challenge to overcome during the initial operation. On the other hand, your system cycles frequently to provide thermal insulation, maintaining heat in between cycles. As a result, the system will have to overwork to cope with the ductwork's temperature.
Ductwork also leaks at the joints. Any air loss means the system will take longer to provide enough hot or cold air to the surroundings. Insulation helps seal these leaks, increase airflow, and improve the system's overall efficiency.
Different Types Of Duct Insulation
For HVAC ducts, only a few types of insulation are used. However, it is often impossible to see the insulation because ducts are installed above the ceiling.
Insulation is usually applied outside ducts to prevent energy loss and condensation. However, it is sometimes used inside ducts to reduce noise, particularly in air-handling unit ducts.
So, without further ado, here are the most common insulation for ductwork.
1. Fiberglass Insulation

Fiberglass insulation is available in two varieties: flexible and rigid.
Flexible fiberglass air duct insulation wraps around ductwork. The visible outer backing has foil for support. The foil acts as an insulator and helps to keep the fiberglass intact. Technicians wrap some industrial-strength tape around the air duct insulation to keep it in place.
For rectangular ducts, rigid board insulation works well. Clamps or clasps secure the rigid board insulation to the ductwork. Fiberglass is one of the most efficient insulation materials available.
You can request the services of professionals to inspect your ductwork. They help determine whether fiberglass duct insulation is appropriate for your building.
Click here to see this product on Amazon.
2. Polyethylene Insulation Foam

Polyethylene (PE) insulates air conditioning and exhaust ventilation ducts. When the duct is exposed, it is preferable to use polyethylene insulation.
It is a more expensive insulation, so concealed ducts use Polyethylene foam for insulation. Polyethylene-insulated ducts are more appealing than fiberglass-insulated ducts because they don't wrinkle and are less hazardous to work with.
Have a look at this product on Amazon.
3. Rockwool Insulation
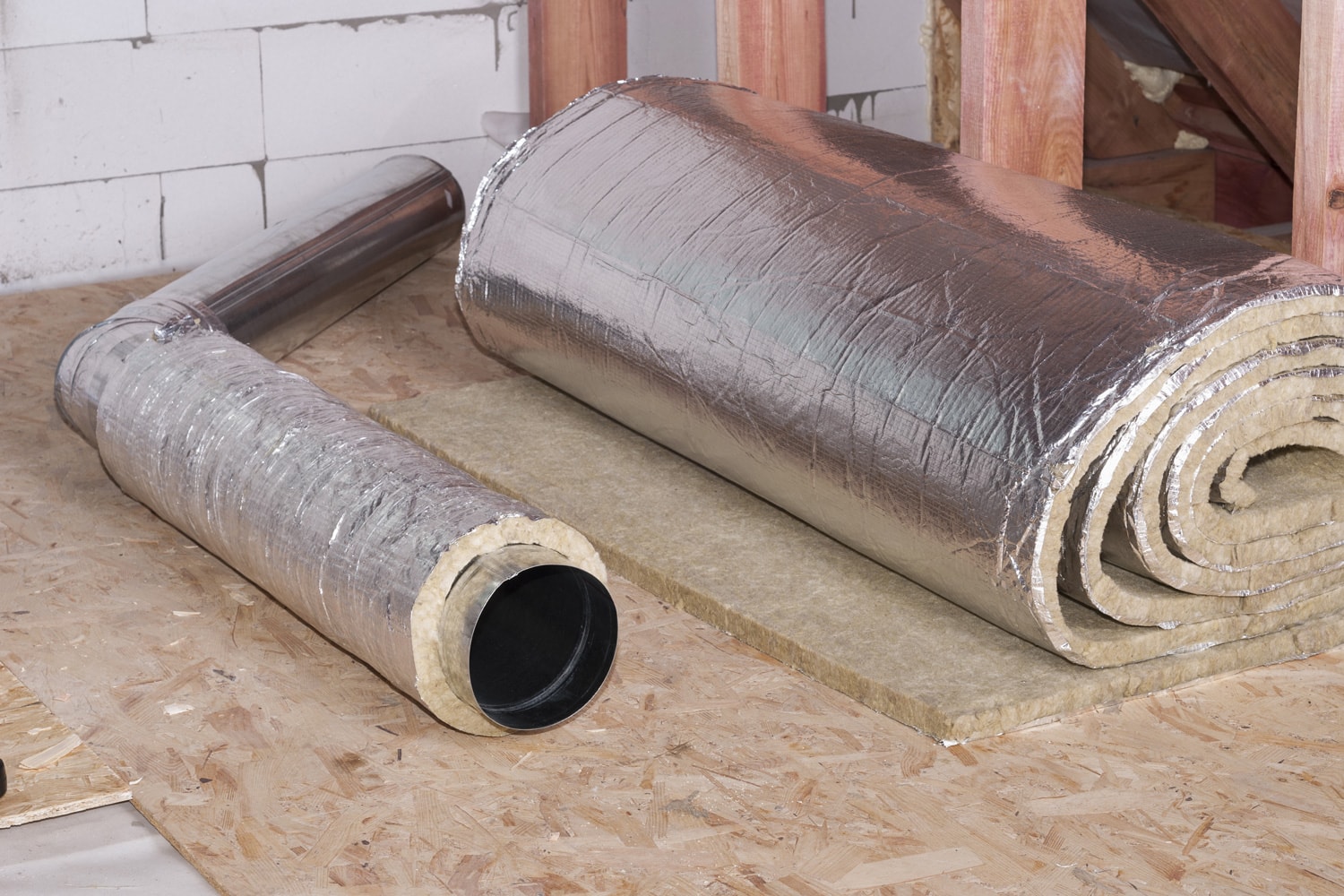

Rockwool is a common sound-insulating material used on the inner surfaces of large air conditioning ducts for soundproofing. Experts sometimes replace Rockwool with fiberglass that meets the exact specifications.
However, Rockwool is preferred because it does not tear easily in the high wind speed inside AHU ducts.
Check out this product on Amazon.
How Long Does Insulation Ductwork Last?

Even though it has a maximum lifespan of 20 to 25 years, most ductwork lasts 10 to 15 years. It frequently begins to deteriorate much sooner because it moves.
Aside from the expansion and contraction caused by temperature changes, vibrations from the fans pressuring air through the house cause damage. The system's metal can also rust. It occurs primarily in the summer when the cool air passes through the ducts causing condensation on the metal.
Rust can corrode the metal to the point where it creates holes in the work, reducing the efficiency of the HVAC system even further. Leaks can also have an impact on air quality. Dust can enter your system if the system runs through the attic.
Dirt, mold spores, and other particles are in the ductwork if it runs through a crawlspace. These contaminants bypass your air filter, potentially degrading the air quality in your home significantly.
What Are The Benefits Of Ductwork Insulation?

Your air ducts are as crucial as your home's heating and cooling equipment. Indeed, even the most expensive, top-of-the-line heating and cooling system will not function properly with poorly designed or improperly installed air ducts.
Even if you check all the boxes, uninsulated ductwork can cause energy loss, condensation, mold growth, and other problems.
Check out these few benefits of insulating your ductwork.
Energy Efficiency
In some instances, ducts run through climate-controlled areas of a building, while others through unconditioned spaces. The process enables designers to maximize usable space while concealing unsightly ducts.
Uninsulated ducts running through unconditioned areas of a building are a common source of inefficiency. The more significant the temperature difference inside and outside the duct, the more energy you lose. The duct unintentionally acts as a heat exchanger, lowering the efficiency of the conditioned air.
Insulating sections of unconditioned ducts reduce energy loss. Hot air remains hotter and cold air remains colder as it travels to your rooms. As a result, you will most likely see significant savings on your energy bills.
Noise Reduction
Uninsulated ductwork can be pretty noisy. That could be due to the normal sounds of your HVAC system moving air through the ducts.
Additionally, there's noise transfer when ducts pick up sounds from one room and transfer them to another. You reduce these noises significantly by adequately insulating your air ducts.
Prevents Condensation
Installing adequate insulation in your HVAC system reduces the risk of condensation due to air transfer. The moisture can cause mold growth and other issues if condensation forms in your ductwork. Certain types of insulation prevent this from happening.
Prevents Mold And Fungus Growth
Moisture from condensation can cause the growth of fungi, mold, mildew, and other microbes. Air duct insulation reduces condensation around air ducts and the likelihood of mold, mildew, or fungus growth at the ductwork's edge.
Given the benefits listed above, it is clear that a duct system with insulation can lower your utility bills and prevent energy waste.
How To Clean Your Air Ducts

Cleaning your air ducts is an efficient way to improve your home's air quality. At the same time, air duct cleaning reduces energy bills by improving the cooling system's efficiency.
1. Turn Off The Power
Turn off the power to the connected air conditioning and heating systems at all times. It prevents the risk of electrocution or accidents.
2. Remove The Cover Or Grilles
Unscrew the air duct grilles or covers with a screwdriver. After you've removed them, thoroughly clean them in a container with hot, soapy water. Allow them to dry completely.
3. Use The Drill
A drill with a brush is an easy way to loosen dirt, dust, spider webs, and possibly mold. Locate and open the register-which are sometimes on the floor or the wall. Push your drill brush into the duct after opening the register.
Turn on the drill and sweep the brush through the ducts. Slowly pull it back while the drill is running. You will also clean the walls of the duct.
4. Use The Vacuum
Insert your vacuum with the brush attachment into the duct and vacuum up the loose gunk. The hose should be sufficiently long to reach deep inside the ducts. Mold, dust, debris, or spiderwebs may be hiding deep inside, making this the only way to get them.
5. Closing Up
After you're finished, replace the register and secure it. If you've previously washed the grill, ensure it's thoroughly dry before returning it. Reconnect the power and check the vents. You may find some loose dust emitted, but it gets contained quickly.
Conclusion
All supply ducts must be insulated. It is also applicable to return air ducts that do not run through a conditioned space. So, if you notice that your return duct needs to be insulated, address it immediately to avoid increasing your electricity bill.
If you find this article informative, please check out these related articles: