Fiberglass is a very durable and versatile material known for its strength and versatile application. However, when it gets wet, its use might not be as efficient. If your home's insulation is made of fiberglass and it accidentally comes in contact with water, here's what to do, according to HVAC experts.
Try drying out your fiberglass insulation as best as you can. Using a fan or a dryer can assist in drying the area if it is in your crawl space or attic. If at all feasible, hoist the damaged batts and store them in a warm, dry place to help them dry out. If you smell any odor, it can be a sign that the fiberglass has to be replaced because the wetness must have caused permanent damage.
We have provided you with more information on how to deal with wet fiberglass insulation. So keep reading to learn more.

Fiberglass Insulation [Features and Uses]
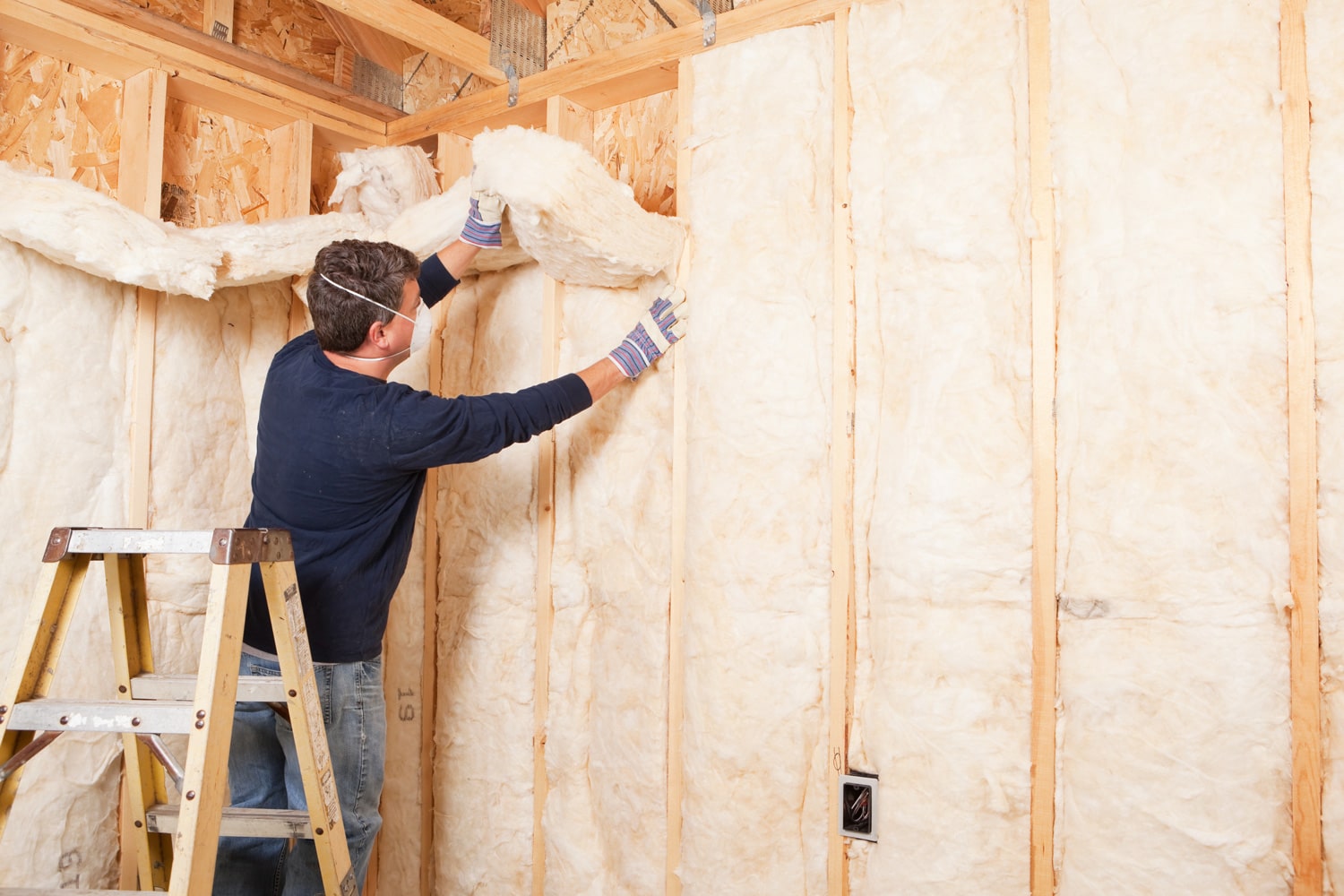

The majority of homes use fiberglass for insulation, a type of insulation made of thin glass strands. It is frequently used in two forms of insulation: loose-fill and batts and rolls. Additionally, rigid board and pipe insulation are both options.
Both home and industrial insulation projects use fiberglass to reduce the transmission of heat and cold. For homeowners wishing to save a little money or perform the placement as a do-it-yourself effort, fiberglass is a good alternative.
The movement of cold, heat, and sound in structures is slowed by the insulating properties with fiberglass. By creating air pockets, the material achieves this, keeping spaces warm during the winter and cool in the summer.
Features
- Mechanical toughness: Steel is more susceptible to corrosion than fiberglass.
- Electrical properties: Even at modest thicknesses, fiberglass is a good electrical insulator.
- Incombustible: Fiberglass is naturally incombustible because it is a mineral-based substance. It does not help a flame grow or continue. When heated, it does not produce smoke or harmful substances.
- Dimensional stability: Fiberglass is resistant to changes in humidity and temperature. Its linear expansion coefficient is small.
- Usability With Binders: Fiberglass can be made in a variety of sizes and can combine with a variety of synthetic resins as well as some mineral binders like cement.
- Non-rotting: Fiberglass does not rot and is unaffected by rats, insects, or other organisms.
- Low Thermal Conductivity: Fiberglass has a low thermal conductivity, making it very valuable in the construction business.
- Dielectric: Fiberglass is useful for electromagnetic windows because of its dielectric permeability.
Uses
- Manufacturing: Grit is incorporated into the surface of fiberglass grating to prevent slipping in damp conditions or regions with hydraulic fluids or oils.
- Power Generation: Due to its non-conductive qualities, fiberglass is used in many components of the power generation industry, including tank farms, scrubbers, and others.
- Automotive Industry: Fiberglass is widely used to create vehicle and body kit parts and accessories.
- Aircraft & Defense: Fiberglass is utilized in the production of test instruments, ducting, shelters, and other components for the military and commercial aerospace industries.
- Securing Fountain & Aquarium Rocks: it aids in circulation and water filtration from beneath the rocks. Fiberglass netting is used to shield spray heads and lights from harm where there are sizable public fountains. Additionally, this lessens the likelihood of someone drowning in an aquarium.
- Paper & Pulp: Due to its corrosion protection and anti-slip qualities, fiberglass is employed in many applications and possesses chemical corrosion resistance.
What to Do With Wet Fiberglass Insulation

A busted pipe or a leaky roof could cause the fiberglass insulator in your roof or wall cavity to become damp. It will no longer be effective as an insulator if this occurs. The good news is that once the insulation dries up, it will resume its effectiveness.
One thing to be aware of is when your fiberglass batts or loose-fill insulation are completely submerged in unclean water, they will soak completely, joining the fibers together and forming clumps. However, you will need to replace the fiberglass insulator if it becomes polluted with dirty water.
Install a dehumidifier or a fan in the area to aid in the drying of fiberglass insulation. Remove the damaged batts if you can, and then relocate them to a warm location to dry. Restore the insulator to the walls or floor cavity it originally came from once it has dried.
The fiberglass might start to smell funny after a few weeks, which indicates that it was polluted with dirty water. Check the fiberglass again, then. To prevent it from damaging your interior air quality, you should replace it completely.
Inspecting and Dealing With Wet Fiberglass
While a professional might use a moisture meter to find dampness in a wall, you might need to access the wall cavity to see whether it is damp and give the insulation and surrounding materials time to dry.
If the insulation is wet from the interior of a wall (for instance, from a pipe leak in the wall), and it doesn't dry out within two to three days, it needs to be removed. Make sure to turn off the electricity to the affected area before doing this.
You may want to initially attempt removing the baseline trim and cutting the plasterboard just high enough just to remove the damp insulation to avoid a complete wall reconstruction. Before closing the wall, let the wall cavities dry out. Replace the wallboard after that, and use broader baseboard trim to cover the exposed drywall.
Before closing the wall, let the wall cavities dry out. Replace the wallboard after that, and use broader baseboard trim to cover the exposed drywall. Both the damaged fiberglass insulation and the wallboard need to be removed as quickly as possible if the insulation was wet from water that was contaminated in any way, such as flood water or sewage.
Flood water carries potential pollutants that could get stuck in the insulation and wallboard and stay there even after the water has evaporated. To prevent inhaling the fibers, don't forget to use protective gear, including gloves, eye protection, and a mask.
Does It Matter If Insulation Gets Wet?
Glass fiber is used to create glass fiber insulation, which momentarily loses its heat resistance when it becomes wet. It will still function as an insulator, though, assuming it can dry out and hasn't already compacted.
In a closed wall cavity, wet insulation typically takes longer to dry out. A wall's damp insulation will sink to the bottom and wet the wallboard and supporting elements.
In addition to decreasing the insulation's ability to insulate, moisture that has been present for even a short period may not dry quickly enough to prevent the growth of mold and wood deterioration.
How Long Does Wet Fiberglass Take to Dry
If the insulation is wet from the interior of a wall and it doesn't dry out within two to three days, it needs to be removed. Make sure to turn off the electricity to the affected area before doing this.
Can Wet Insulation Cause Mold?
The answer is yes, but it is vital to note that insulation doesn't provide mold with any nutrition. Even cellulose insulation, which is just paper that has been ground up, has a lot of fungicide and fire retardant compounds, making it unattractive to mold.
Almost all types of insulation are susceptible to the growth of mold. Insulation is not what the mold feeds on; rather, it feeds on dust in the air that adheres to moist or wet insulation.
How Long Does Fiber Stay in The Air?

Because glass fibers are purposefully broken up by producers to make them shorter, only a small portion of them are respirable. In other words, the majority of the fiberglass fibers will be quickly ingested and expelled from your body before reaching your lungs.
They can stay in the air for up to several hours and are also invisible to the naked eye and as such may not be cleaned up by your regular cleaning agents or equipment. However, for effective cleaning, a ULPA or HEPA vacuum cleaner is recommended.
Is Exposed Fiberglass Insulation Harmful?
Due to variable test findings for different types of fiberglass insulating materials, fiberglass was originally classified as a carcinogen; however, as of 2011, this data has been withdrawn. However, there is now no conclusive proof that fiberglass induces cancer in people.
Should Exposed Fiberglass Insulation be Covered?
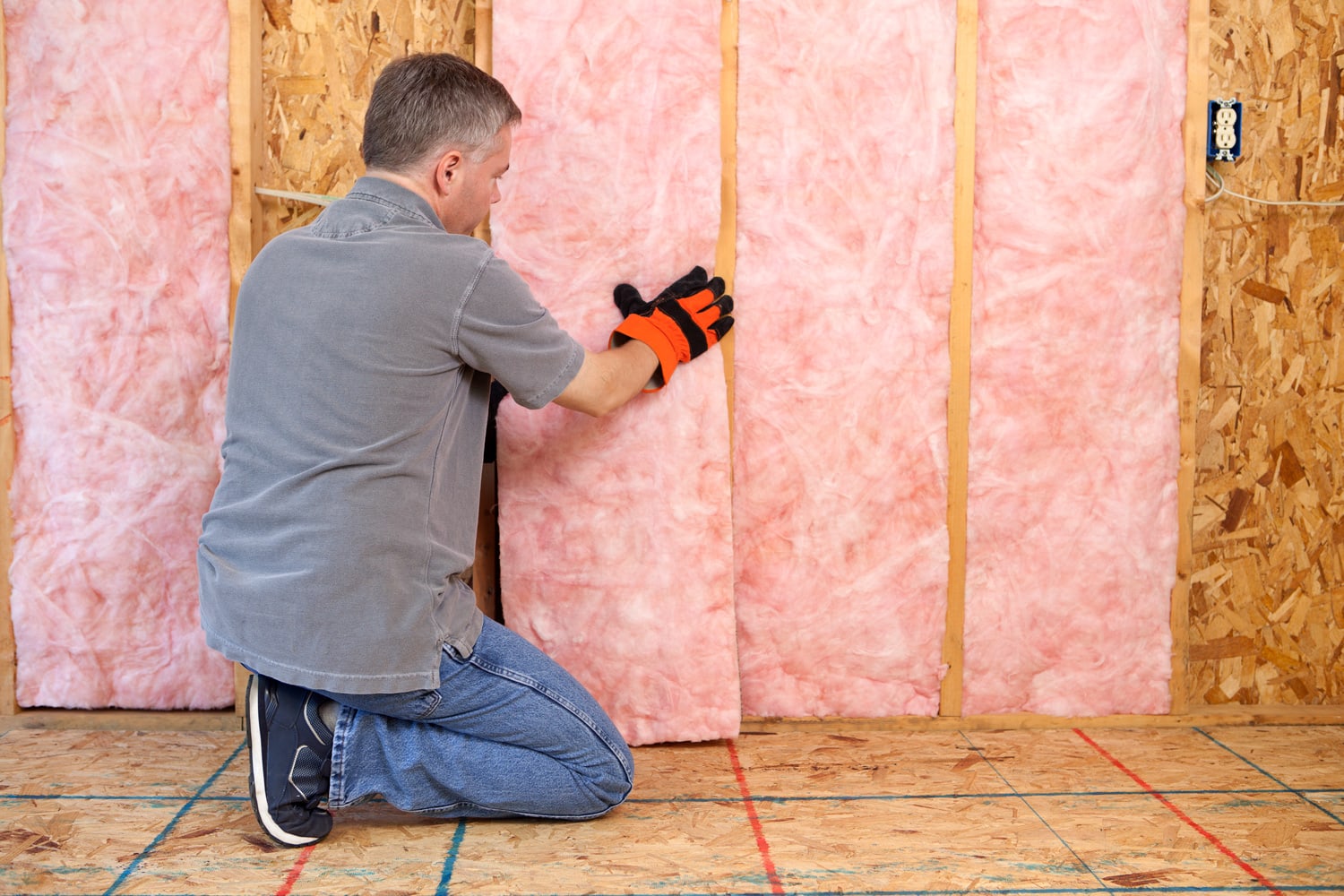

The strategy relies on how you intend to utilize the area where the uncovered fiberglass is situated. Homes frequently contain attics or basements with exposed fiberglass insulation. Pink, fluffy batts that are neatly tucked between walls, rafters, and beams insulate the room from temperature variations outside -the exposed insulation should not pose harmful.
However, if the area will receive a lot of day-to-day activity, it is recommended to cover the exposed insulation so as not to damage it. Also, direct contact with the fiberglass fibers could cause skin irritation, so it should be avoided.
To Wrap Up
Insulating your home is one way to make sure it remains at the same temperature all year round. With the information provided above, we trust that you should be able to make informed decisions should you be faced with the challenge of dealing with wet fiberglass insulation.
For more on fiberglass insulation, read these interesting articles: