Different types of insulation are used in the construction of homes to help keep moisture and air out and regulate the interior climate. However, you may wonder if any natural materials can be used as insulation.
We researched different types of natural insulation. These are just as effective as fiberglass or insulation made from polymers. These are forms of insulation derived from animals, plants, and other eco-friendly materials.
If you are curious about natural materials that can be used as insulation, check out our list of suggested products.
- Castor Oil [Icynene]
- Cellulose
- Cotton
- Grass
- Hemp
- Perlite
- Rice Stalk [MDF Boards]
- Sheep's Wool
- Soybean
- Straw
- ThermaCork
Because many types of commercial insulation may contain formaldehyde or other undesirable elements, natural forms of insulation can prove better for human health and the environment.
![Loose-fill fiber and sheep wool insulation in walls, What Natural Materials Can Be Used As Insulation? [10 Good Options]](https://hvacseer.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/What-Natural-Materials-Can-Be-Used-As-Insulation-.png)
About Natural Insulation
Since early humans began constructing homes to live in, people worldwide have sourced natural materials to insulate their structures. Without proper insulation, houses may be unbearably cold or hot or suffer moisture damage.

We will explore a range of different natural materials that prove to be high-quality forms of insulation. Many natural forms of insulation are eco-friendly. They offer a significant R-value, are sustainably sourced, and do not pose health risks.
1. Castor Oil [Icynene]
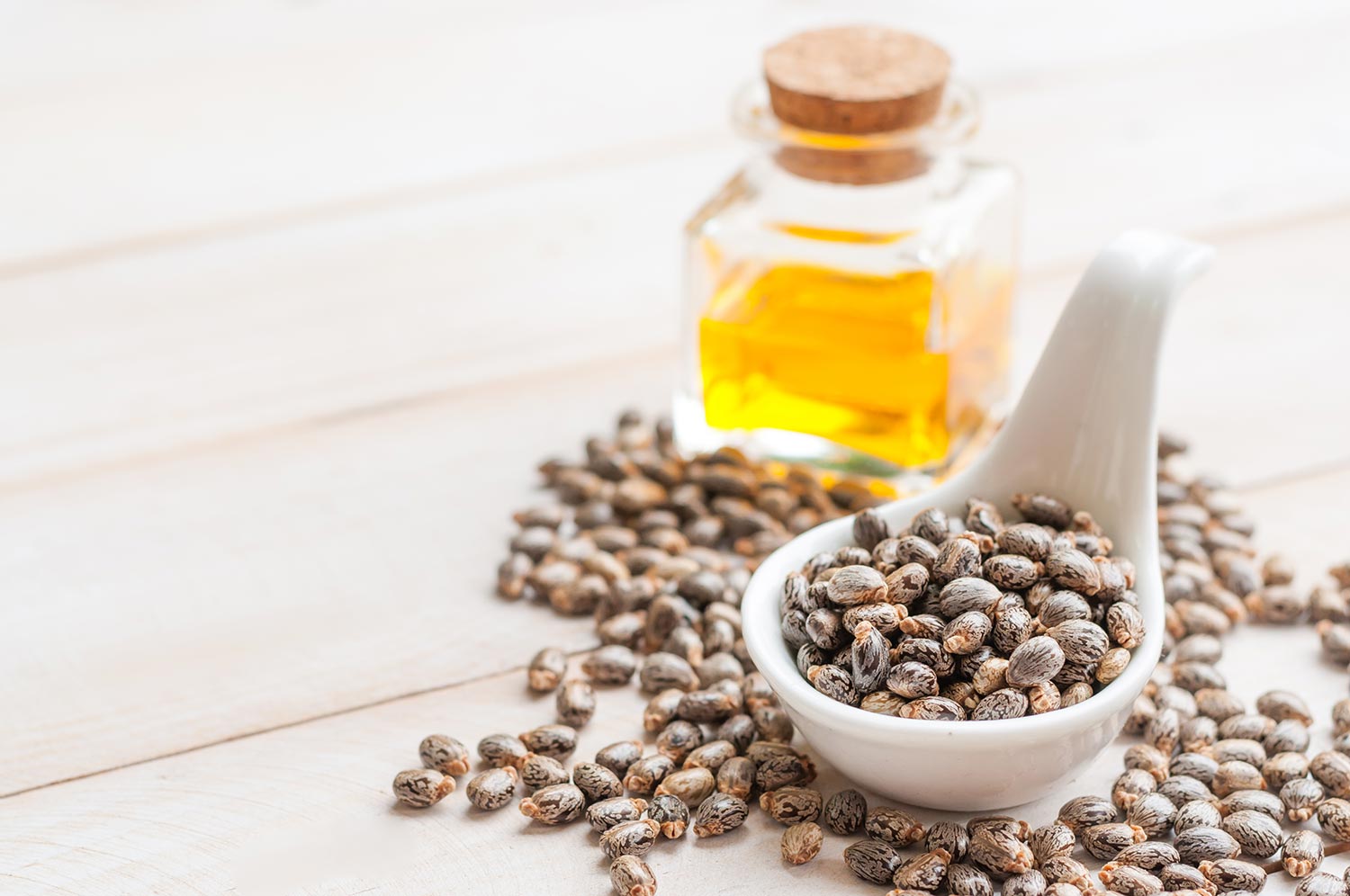

Believe it or not, there is thermal insulation derived from castor oil that is rigid foam insulation used for roofs. There is also a castor oil-derived spray foam insulation, also known as Icynene.
Icynene is a non-toxic, eco-friendly form of insulation that is blown in with water. It is available in low or medium density, and poses no health risks to indoor air quality. The R-value ranges from 3.7 to 36, depending on the thickness.
2. Cellulose
Instead of lingering in landfills, recycled paper gets ground down into cellulose insulation. It is used for attics, open walls, and existing closed walls in homes. Blown-in cellulose can be homemade or is often commercially produced.
Cellulose insulation has a similar consistency as down feathers and provides plenty of insulation with a dense composition.
3. Cotton

If you are looking for insulation with a similar performance to fiberglass but with fewer health risks, check out cotton. Old denim and other cotton-based fibers are ground down to create blown-in or batting insulation.
Installation of this insulation doesn't pose skin irritation, require interaction with formaldehyde, and fibers don't get released into the air. Although cotton insulation is more expensive, it is a healthier option for people and the planet.
The R-value for cotton insulation ranges from 3 to 4 per inch, so more layers may be needed than other materials.
4. Grass
As people seek to lower their carbon footprint, grass is proving a valuable material to create insulation with an R-value of 3.5 per inch. Grass insulation requires less water to manufacture than fiberglass and is treated for fire retardation.
Grass insulation is stable and mold-resistant. It doesn't present certain health hazards like conventional insulation, but it is more expensive and harder to find.
5. Hemp
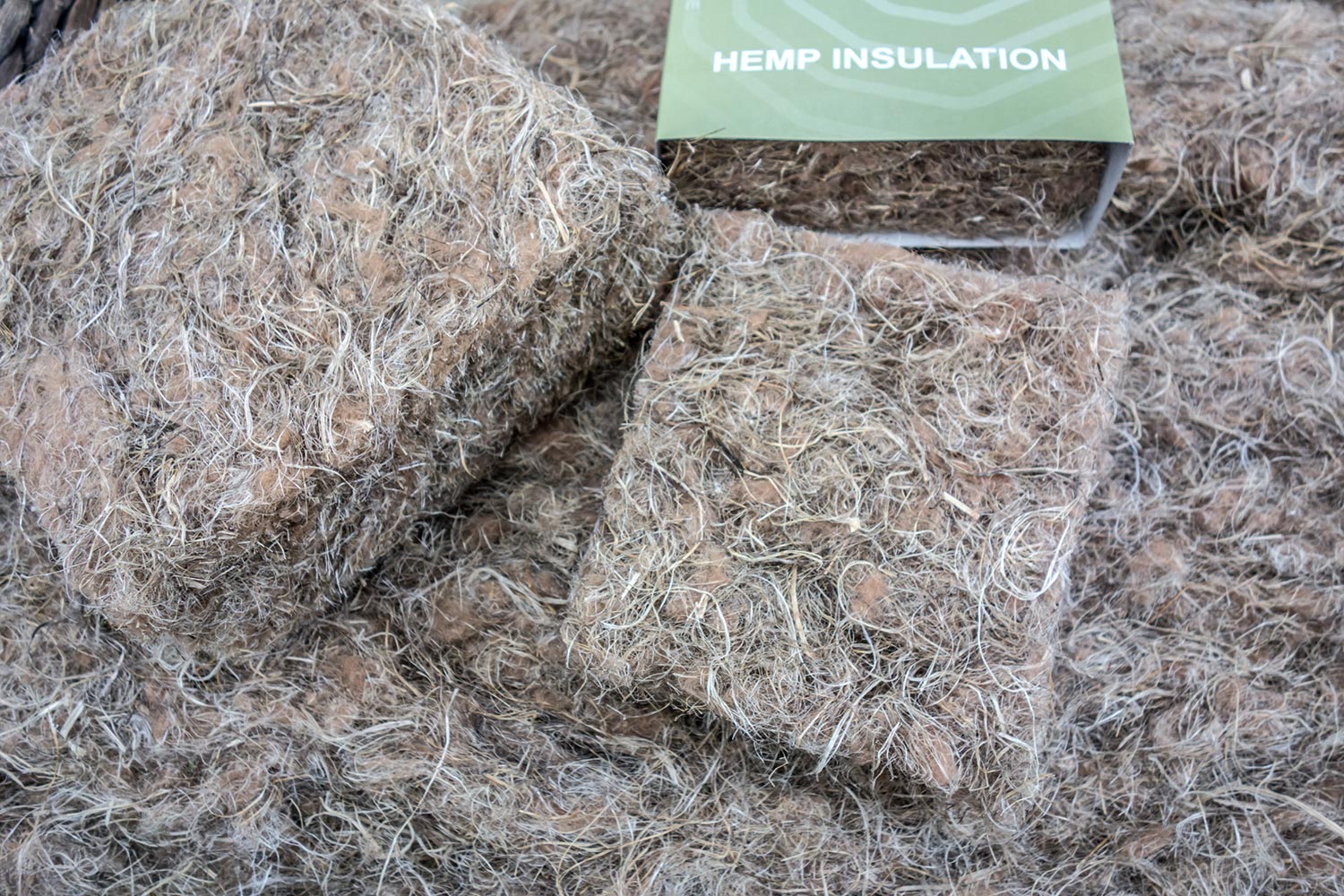

A sustainable and durable form of insulation used as an alternative to fiberglass batting or foam insulation is made from hemp. There are forms of hemp insulation available as a roll of felt or semi-rigid sheets.
If hemp insulation gets wet, it can be removed and allowed to dry and then replaced without losing performance. There are no chemical binders or harsh VOCs involved in manufacturing hemp insulation, and it is biodegradable.
Additionally, hemp insulation repels rodents and insects. It may have an R-value ranging from 13 to 20 if it is 3 1/2 to 5 1/2 inches thick.
6. Perlite
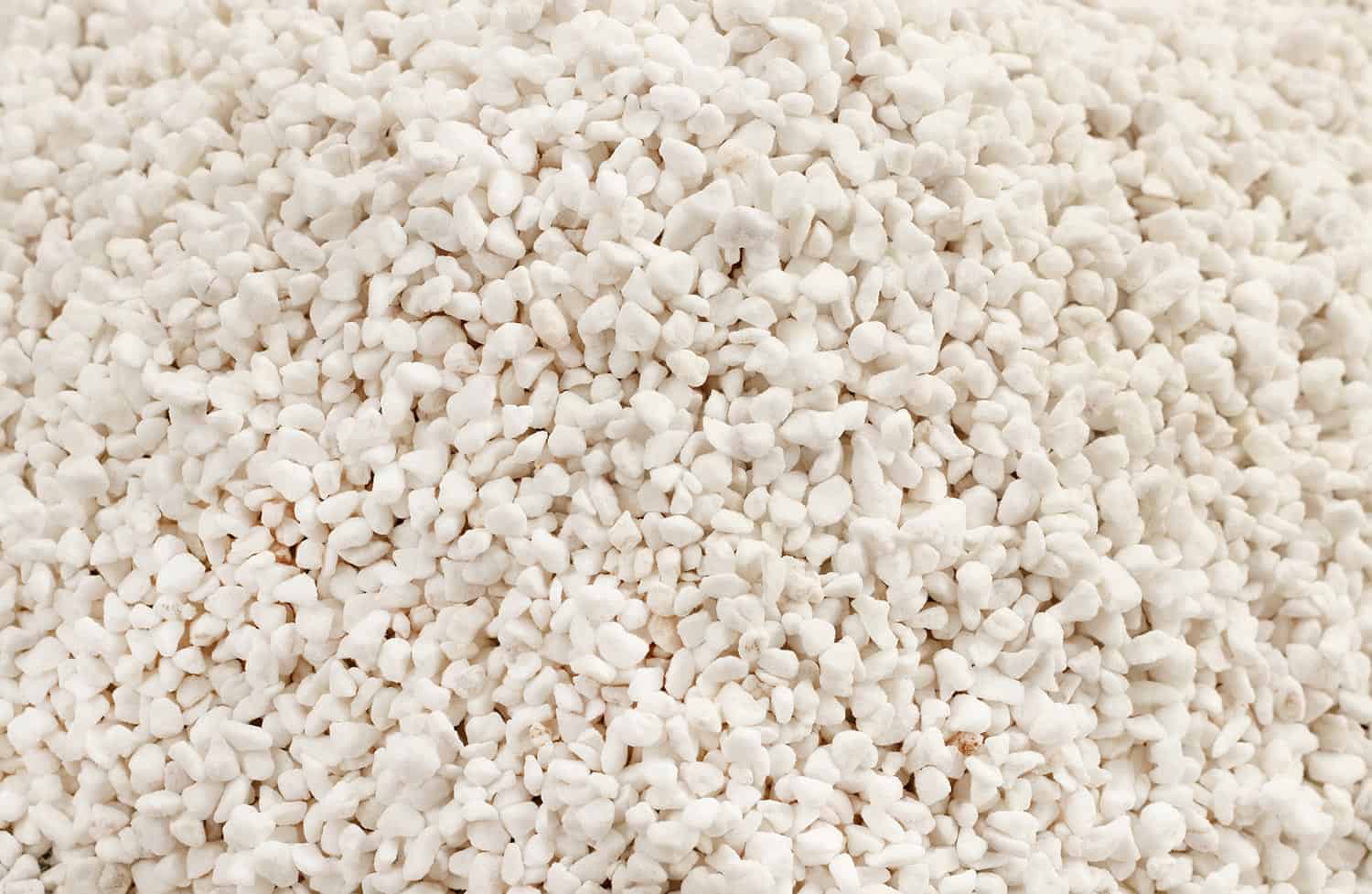

Perlite is a desirable form of insulation because it doesn't rot or create a friendly habitat for rodents and has an R-value of about 2.7 per inch. This insulation is derived from volcanic rock and has a high thermal resistance.
Perlite may be mixed in with concrete to improve thermal resistance and soundproofing. However, this material is usually placed behind concrete slabs, within chimneys, or with pizza ovens.
7. Rice Stalk [MDF Boards]
Rice straw or rice stalk has been typically left behind as a waste product with no practical application. However, one company, CalPlant, has begun producing medium-density fiberboard insulation using this material.
The unique rice boards are similar in construction and density to their wood composite counterparts, except a non-formaldehyde binder is used for this product.
8. Sheep's Wool
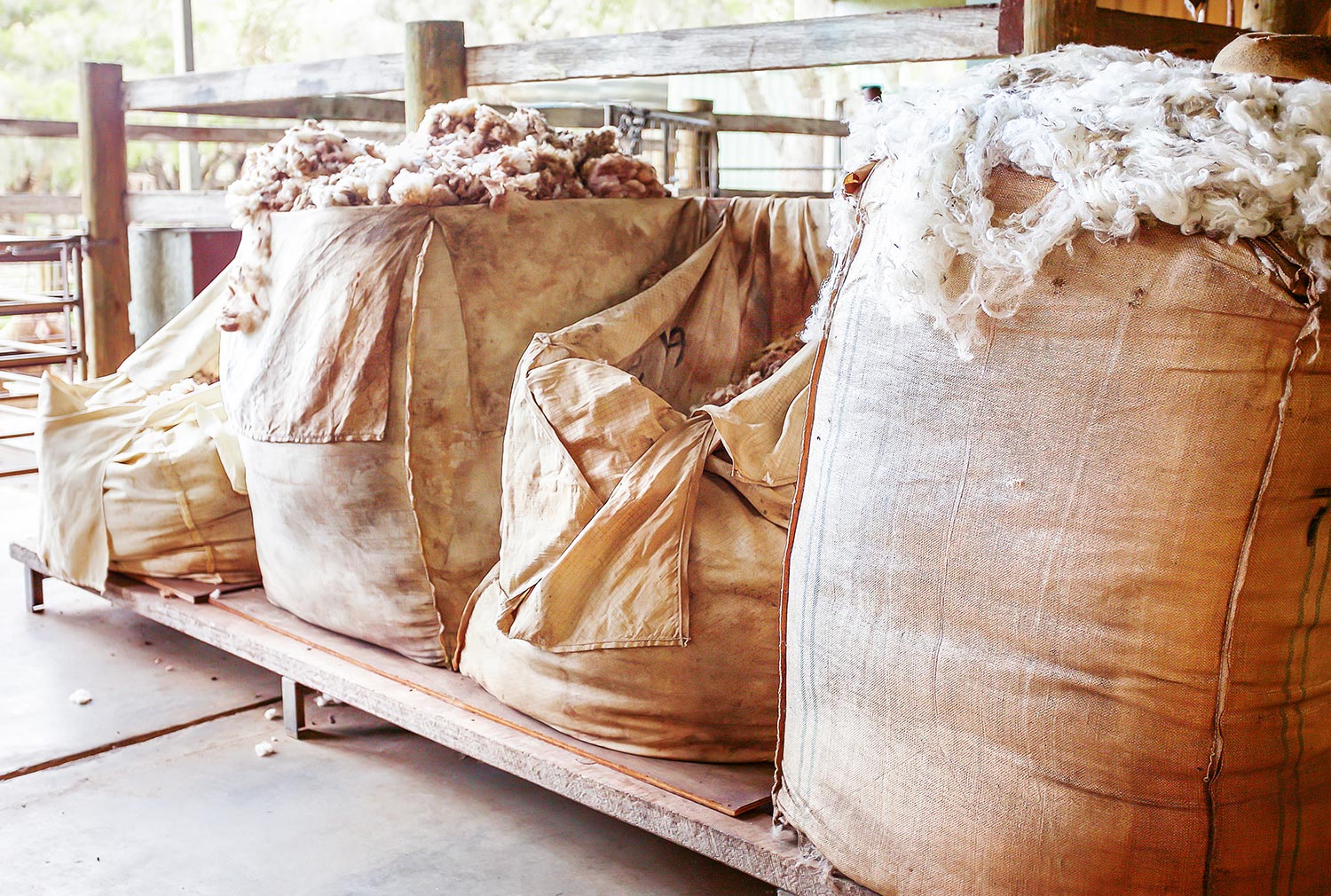

A fantastic natural insulator for homes is sheep's wool. This animal-based product is devoid of VOCs, is sustainable, and has an R-value between 13 to 19 per inch, which is on par with fiberglass and mineral wool.
The unique properties of sheep's wool make it resistant to mold and fire, plus it dampens sound, handles humidity well, and doesn't break or tear easily.
9. Soybean
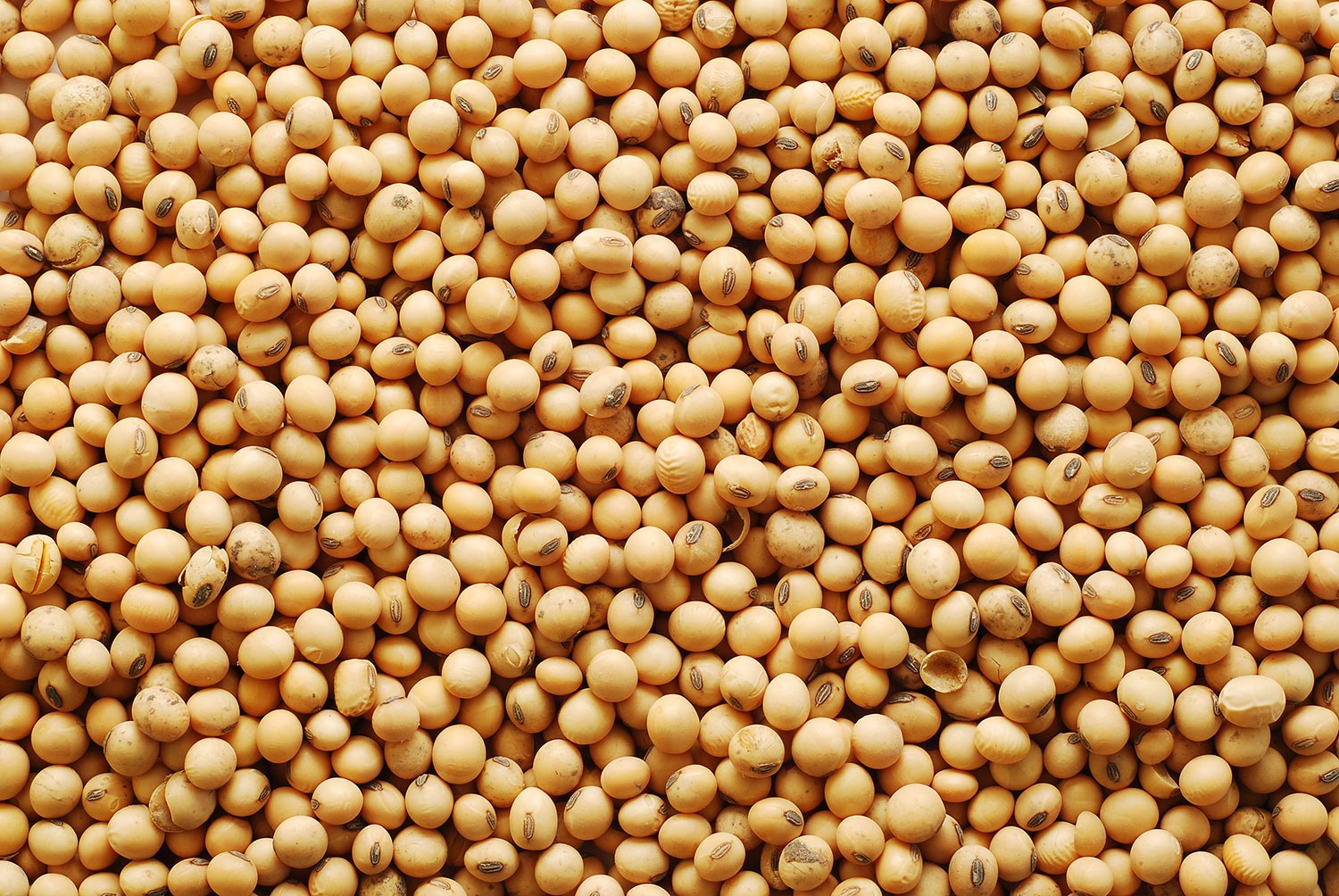

Move over tofu and soy sauce, soybeans have proven their worth as an insulation material. Yes, insulation made from soybeans is unique for its ability to expand nearly 100 times its size when blown into walls as spray foam.
However, soybean foam is worth a bit of investigation; it is mainly comprised of petroleum. But, one redeeming factor is that soybean-based foam insulation is free of hydrofluorocarbons, formaldehyde, and urea, and it resists moisture.
10. Straw
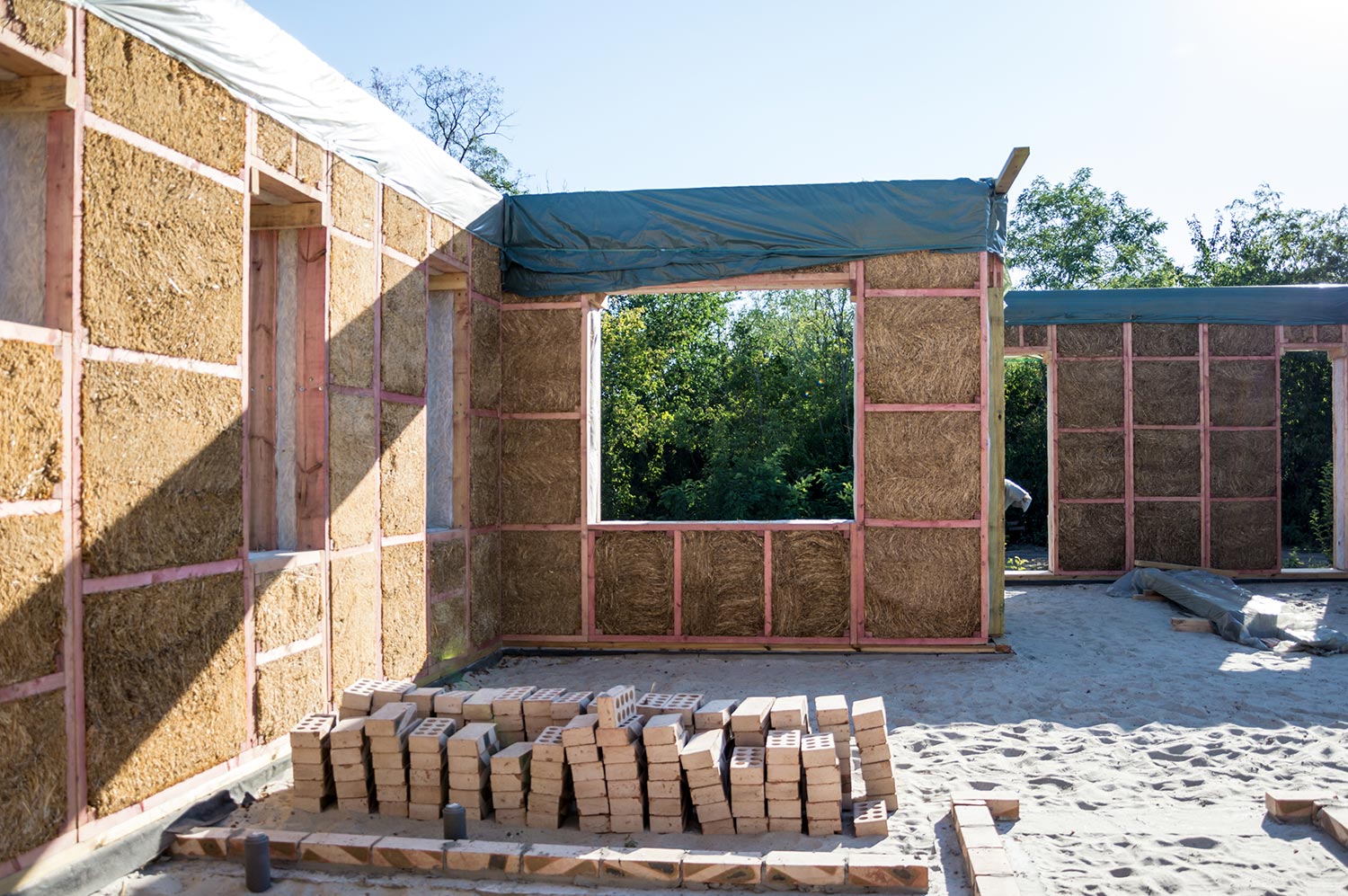

The use of straw as a construction material is nothing new, as it is naturally renewable, promotes healthy indoor air, and is an excellent insulator. Either bales of straw or straw-based insulating boards are used to build homes.
Straw insulation has a very high R-value, is fire-resistant, and has impressive soundproofing qualities.
11. ThermaCork
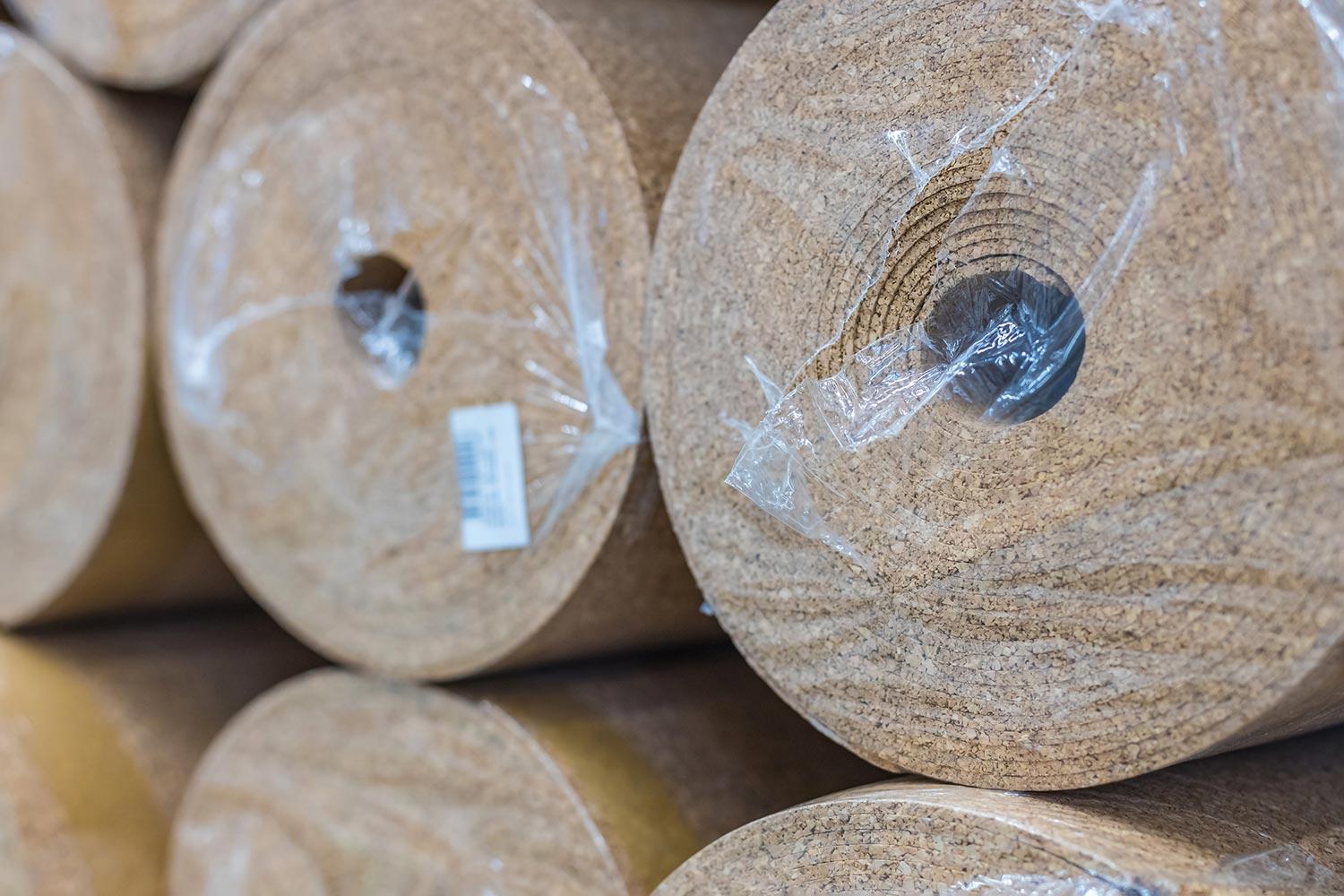

Cork is another wonderful plant-based material useful for underlayment for flooring and as a natural thermal insulator. You can find rolls or panels of cork or a spray form of insulation composed of cork and polymers.
As an insulator, cork has an R-value between 3.6 and 4.2 per inch, and it is a fire, mold, and mildew-resistant material.
Is Styrofoam Good Insulation?
Because of the unique composition of styrofoam, it is excellent at trapping air within small pockets of space, reducing heat loss. Depending on the thickness of styrofoam board insulation, this material has an R-value of 3.6 to 4.2 per inch.
Check out this styrofoam insulation board on Amazon.
Is Wood A Good Insulator?
A light, dry wood is a good insulator for cold weather and performs better than glass, brick, or concrete. However, compared to fiberglass, wood is not better at reducing heat loss or trapping air.
Because the fibers of wood are densely packed, it won't allow energy to quickly leave from home, although it is a slightly porous material.
How Do You Make Homemade Insulation?
Try your hand at creating cellulose insulation with the help of a hammermill and plenty of old cardboard, newspapers, and other paper materials.
You'll want to grind up your paper as finely as possible and add in a repellent for pests, vermin, and a fire-retardant. A wonderful benefit of homemade cellulose insulation is that you get an R-value of 4 for every inch of processed fiber.
Some suitable materials to use to treat your homemade cellulose insulation include borax, aluminum sulfate, and a bit of lime. This type of insulation is best used in areas that will stay dry and are unlikely to become moist.
What's The Cheapest Way To Insulate?
Fiberglass batting is one of the most inexpensive materials to insulate a home's walls. However, if you are looking for natural insulation that is budget-friendly, the cheapest is perhaps blown-in cellulose insulation.
Cellulose insulation is desirable for closed walls and attic spaces, as its tightly packed fibers help close off any air that would feed a fire. Plus, cellulose is composed chiefly of ground-up paper or denim and is treated with non-toxic materials.
Check out this cotton insulation on Amazon.
Conclusion
We hope you discovered some fantastic options for natural insulation for your home or property. Using natural insulation is an excellent way to avoid introducing potentially hazardous chemicals to your home and is eco-friendly.
Depending on your home's layout, where you need insulation, and the desired R-value needed, different natural materials may be better than others. Check out natural insulation made from animals or plants and feel the difference.
Before you go, you won't want to skip reading the following articles.