When installing an HVAC unit, having a properly sized duct system is as important as choosing the right air conditioner size. You may be wondering what size duct system should be used with a 3-ton unit. We've researched this question and have information to share below.
As a general rule, the supply duct size for a 3-ton AC is as follows:
- Round duct - 16" diameter
- Rectangular duct - 16" x 12" or 20" x 10" or 24" x 8"
For the return air duct, experts agree that it should be larger than the supply duct, measuring as:
- Round duct - 18" diameter
- Rectangular duct - 16" x 15" or 17" x 14" or 20" x 12"
Note: Rectangular ducts come in different dimensions but you can choose from any 0f them as long as the square inch measurements (length x width) are roughly the same.
In the duct sizes shown above, for example, the areas in square inches are 192; 200; 192 for supply ducts and 240; 238; 240 for return ducts.
As a homeowner, having a basic knowledge and understanding of HVAC ductwork makes you confident enough to ask questions and participate in the discussion with an HVAC expert. Read on to learn about types of ducts, why duct size is important, and how to make sure you get the right size.

Why Duct Size Matters
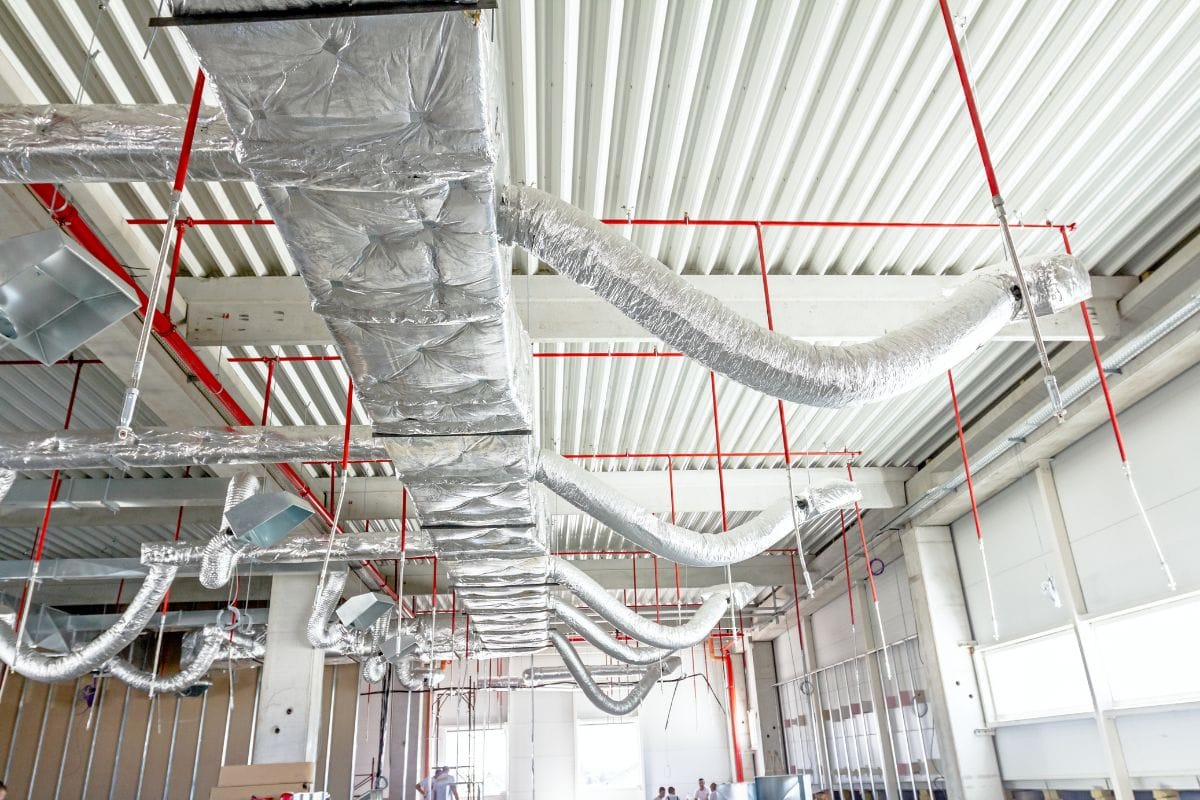

A significant aspect of HVAC installation is ensuring that the ductwork conforms to the standards of proper sizing.
You should avoid generalizations in duct sizing as various factors come into play when determining the correct measurements. HVAC professionals use air duct calculators and sophisticated software to come up with accurate results, and it's best to work with a reputable service provider.
The right duct size moves air into the house and all its rooms in a uniform and efficient manner, maintaining an even temperature throughout the whole space, creating a comfortable environment with clean indoor air, and lowering your electric bill through economical usage.
When your supply ducts are too small, airflow is restricted and pressure builds up in the system. The consequent resistance strains the HVAC components, making them run longer to compensate for the reduced airflow.
At some point, the HVAC system will break down and will need repair or replacement.
Undersized return ducts cannot accommodate enough air to go back into the HVAC to be conditioned and redistributed. To compensate, the system needs to run longer, incurring higher energy consumption.
An oversized duct system cannot build up enough air pressure to move air and distribute it into the house. Hence, the cycle has to keep running to sustain the pressure. The strain of continuous cycling of the HVAC system will wear down and damage the AC and its components.
How to Get the Right Duct Size
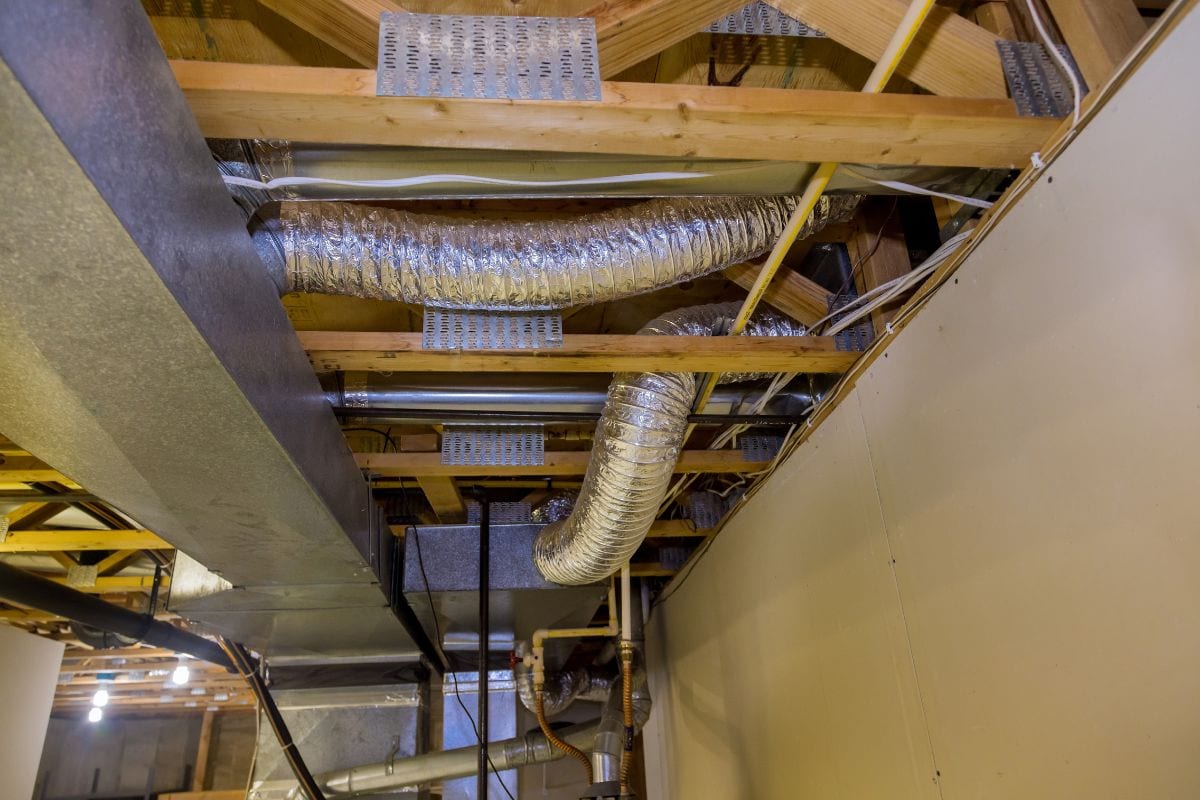

Having the right duct size for your HVAC system is vital for efficient functioning where all rooms are cooled or heated at the desired temperature, air quality is good, and electric power use is economical.
Calculating the duct size of your air conditioner is complicated, involving several elements and mathematical equations. Here is a bird's-eye view of the factors for computing duct size.
Home area
The square footage of your house determines the size of your HVAC unit. Measure the length and width of each room in feet and multiply the two numbers.
The product is your area or square footage. Add the areas of all rooms and you get your house's square footage. A 3-ton AC can comfortable cool a 1,500 - 2,000 sq ft home.
Friction loss rate
As air flows through the ducts of your HVAC system, it rubs against the duct's inner surface and loses pressure. This is called friction loss. Supply ducts and return ducts have different friction loss rates and calculating them is a complex undertaking.
Cubic feet per minute (CFM)
CFM measures airflow. Like friction loss rate, computing for CFM is not simple. Even HVAC experts use a duct calculator to compute CFM.
Manual D is the industry standard guide for residential duct sizing for the different materials for ducts. The ACCA (Air Conditioning Contractors of America) refers to this manual when evaluating homes and granting permits for an HVAC system installation.
Types of Ducts
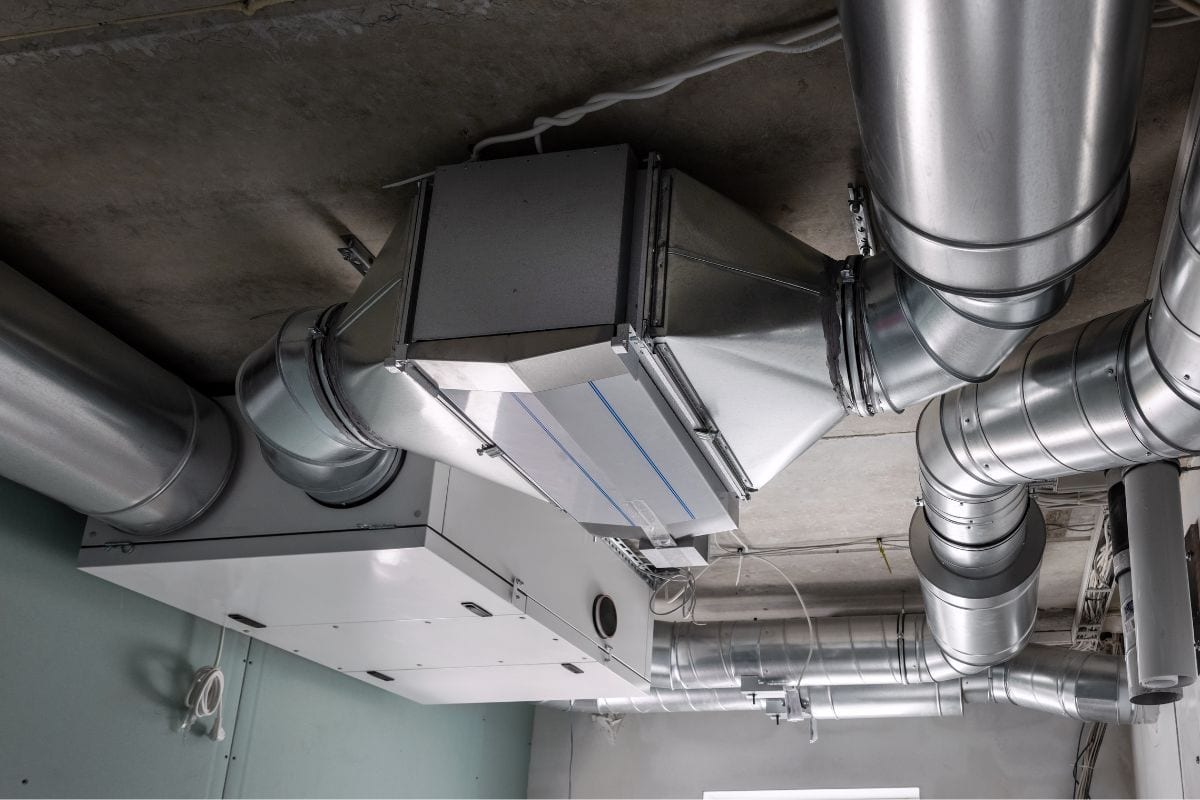

Ducts for the cooling and heating system are classified into two main categories: rigid and flexible.
Rigid ducts are straight and firm. They are the recommended type for the entire ductwork while flexible ducts are bendable and are often used for short duct paths and connecting outlets to rigid ducts. Rigid ducts are made of any of these materials:
Sheet metal
These may be galvanized steel or aluminum. Aluminum ductwork costs more to install than galvanized steel. Its lighter weight makes it easier to handle and install. But it should be thick enough to resist force and maintain its shape in case it is walked on.
Sheet metal ductwork is the most common type. The smooth surface makes for easy cleaning and the nonporous quality deters the growth of molds and mildew, making indoor air safer. Sheet metal ductwork is the most durable type and can last for 20-25 years.
The downside to sheet metal ducts is it collects dust and debris easily.
Fiberglass
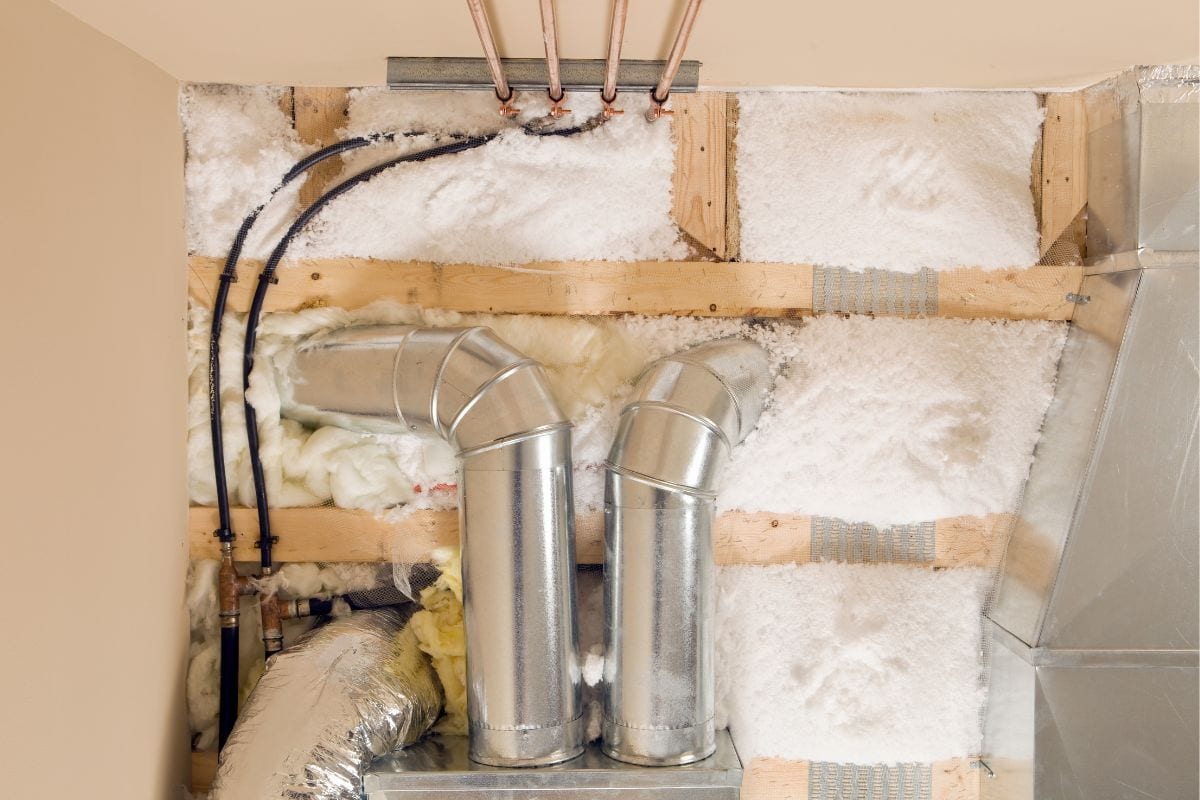

Ductwork made of fiberglass requires less cleaning because of its sealed interior lining. Its insulation promotes even temperature throughout the house and less heat loss, bringing down power usage. A properly sized fiberglass duct system makes less noise.
Fiberglass ductwork can last for 10-15 years, then it starts to deteriorate. Its particles are carried by the airflow and enter the rooms, creating an unhealthy environment that may bring about asthma and other illnesses from inhaling these particles.
Fiberboard
Fiberboard is made from compressed glass fibers glued together by resin. Ducts made from fiberboard are the least expensive and, like fiberglass, are not prone to excessive heat loss or gain. Its exterior has a foil lining to prevent leaks that may allow the entry of heat or water vapor condensation.
The fiberboard duct system has its disadvantages, too. Its rough interior surface interferes with the airflow and is conducive to bacteria growth and molds. The material also deteriorates over time and the minute particles can enter through the vents, contributing to an unhealthy indoor environment.
Flexible ducts
Flexible ducts are made from covered steel spring coils. Their pliability makes them the preferred ducts for tight spaces because they can go around fixtures. Flexible ducts are cheap and easier to install than rigid ducts. They are useful for connecting air supply outlets to rigid ducts.
But the disadvantages of flexible ductwork outweigh its benefits. They are vulnerable and a puncture or snag will make them leak. The crinkles in the inner surface limit airflow. They may eventually sag due to wear. They are easily compressed and are difficult to clean.
How to Calculate Duct Size
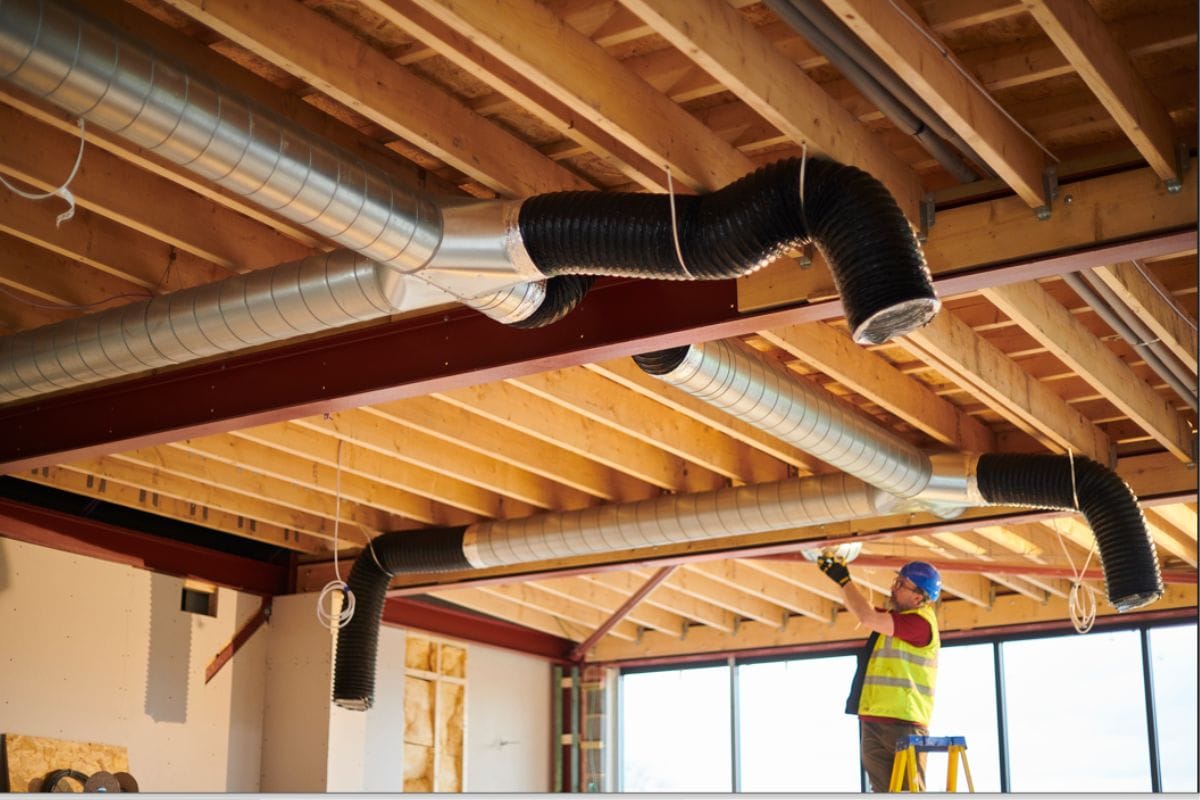

HVAC specialists use a duct size calculator or software program to determine the right size duct for the heating and cooling system of a house. They also have to establish certain values such as the square footage of the space, friction loss, air flow velocity, and static pressure.
An error in any of these formulas can result in undersized or oversized ducts and will ultimately be costly.
Click here to see this air duct sizing calculator on Amazon.
Below is a general overview of the formulas that are entered into a duct size calculator to arrive at the proper size of the ducts for your HVAC:
HVAC size
The size of your air conditioner depends primarily on the square footage of your space. Look up charts online that give you the HVAC size for the square footage of the space. Other variables are considered when choosing your AC sizes, such as insulation and the climate zone of the state.
Square footage
The square footage of a space is necessary for deciding on duct size. This measurement must be taken for the whole house and each room.
The square footage is the product of the length multiplied by the width of the space. You can measure the square footage yourself or you can refer to the blueprint or ask the zoning authority in the local area.
Airflow
Airflow is measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM) which is expressed as volume. To determine CFM, you get the volume of the room, which is length x width x height (or the square footage x height.)
For both square footage and CFM, you can measure irregular-shaped rooms by breaking them up into squares or rectangles and adding them all up.
Final Thoughts
Ductwork sizing for your HVAC size is crucial for the optimum functionality of your heating and cooling system. Knowing the elements involved in calculating duct size does not make us experts. Get the services of HVAC professionals to avoid any mistakes.
Recommended reading: