Radon is hard to detect in homes since you can't see or smell it. You will only know you are being exposed to radon if you test for radon levels, which is not common practice for most homeowners. So, where can you find radon gas in homes? After extensive research, we have finally determined the answer.
You can mostly find radon gas in basements and crawl spaces. These areas are susceptible to radon infiltration due to the cracks and crevices present in their foundation.
There are still other areas in your house where radon can enter. This post will also cover how to be aware of testing the radon levels in your home. Please keep reading, and let's dig deeper to learn more about radon.
![fiberglass insulation and windows in basement, Where Is Radon Found In Homes [Where Is It Most Likely Found In The Home]?](https://hvacseer.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/20.-Where-Is-Radon-Found-In-Homes-Where-Is-It-Most-Likely-Found-In-The-Home.jpg)
What Is Radon?

Radon is an odorless radioactive gas that you can't see. The radioactive decay of uranium is the primary source of radon. In addition to soil and rock, radon can also be present in water.
Radon dispersed in well-aerated outdoor spaces is often non-detectable and poses no threat. Normal radon outdoors levels might be between 5 and 15 Bq/m3.
Mines, caves, and water treatment plants have the most significant radon concentrations because they have the least ventilation. Also, radon is most likely present in basements and crawl spaces in homes.
Radon levels in structures, including houses, schools, and workplaces, can range from as low as 10 Bq/m3 to as high as 10,000 Bq/m3.
People should know everything about radon since this radioactive gas is everywhere and can pose health risks.
Can You Determine If You Are Exposed To Radon?

Unfortunately, there are currently no available medical tests to determine your radon exposure. However, if you are concerned, discuss the possibility of routine health checks and screening for lung cancer with your physician.
The US government founded the Radiation Exposure Compensation Program to help compensate workers exposed to radon on the job. These include uranium miners, transporters, and millers. Those affected by lung cancer or other lung-related disorders that meet the criteria are eligible for settlement.
What Are The Health Effects Of Radon?
Radon's properties mean that people living or working in different structures may be unwittingly exposed to dangerously high radon levels. You may not know it, but you can develop lung cancer because of radon.
When radon decays in the air, it releases even more radioactive particles. If you inhale these particles, they settle on the airway lining cells, which can induce DNA damage and lung cancer in the worst case.
According to the National Library of Medicine, depending on the average radon level and the smoking incidence in a country, there is an estimation that 3% to 14% of lung cancer cases are because of radon exposure.
Extremely high levels of radon exposure were initially linked to an elevated risk of lung cancer among uranium miners. Studies have also proven that in household settings, radon can be harmful to health and contribute to the global increase in lung cancer rates, even in low amounts.
Furthermore, although radon poses a threat to smokers and non-smokers, you must note that radon exposure makes the former more susceptible to lung cancer.
Note the possible signs and symptoms, which include:
- chest pain or tightness
- difficulty breathing or swallowing
- sore throat
- worsening cough
What Are The Factors That Affect The Amount Of Radon In A Building?
Home is where most people spend their time; therefore, that's where they're most likely to get radon exposure. However, indoor businesses can also be a source of exposure. Factors that affect the amount of radon in homes and other buildings include:
- The pace at which air moves from inside space to outside. It relies on factors such as the structure's airtightness, the ventilation patterns of its residents, and the building's structure.
- Potential entry points for radon gas from the ground into the structure
- The local geology also affects the radon concentration. It includes soil permeability and uranium content.
- The release of radon into the air from construction materials
- Cracks and crevices are present in the entire building.
- Gaps or openings in foundations or near pipes or wires
- Water, particularly from deep wells.
Your crawl spaces and basements are especially prone to radon buildup because of their proximity to the ground. The small gaps, cracks, and crevices that are present almost everywhere in your home make it even easier for radon to leak in.
That said, it's still possible to find high radon concentrations above the basement.
How To Test For Radon

Since radon gas is odorless and invisible, testing is the only way to determine your exposure to it. The Environmental Protection Agency issued A Citizen's Guide to Radon, which details how to test your house for radon at little cost and what to do if the radon concentrations are significantly high.
There are two ways to test for radon. You can buy a radon test kit to do the test yourself or hire a radon expert to help you out.
If you choose the former, it would be best to follow the manufacturer's instructions on the product label regarding how long you will need to leave the kit at home in a specified amount of time. After that, send it to a lab and wait for the results.
Click here to check out this radon test kit on Amazon.
Related: "Can You Be In A House During A Radon Test?"
How Often Should You Test For Radon?
Radon levels fluctuate widely from one structure to the next, every day and every hour inside the same building. These variations highlight the importance of monitoring radon for a minimum of 90 days if you want an accurate estimate of the yearly mean radon levels in your home.
EPA suggests in their published A Citizen's Guide To Radon that you should perform radon testing every two years to ensure safe levels. Using modest passive detectors or the radon test kit we have mentioned earlier, you can quickly, easily, and cost-effectively detect the radon levels in a home.
It is essential that you base the measurements on national norms to provide uniformity and dependability for decision-making. When time is of the essence, such as during the evaluation of the efficacy of radon mitigation systems, radon examinations that follow all national regulations are most helpful.
Related: "Should You Buy A House With A Radon Mitigation System? [Important Considerations!]"
What To Do After The Radon Test Results?
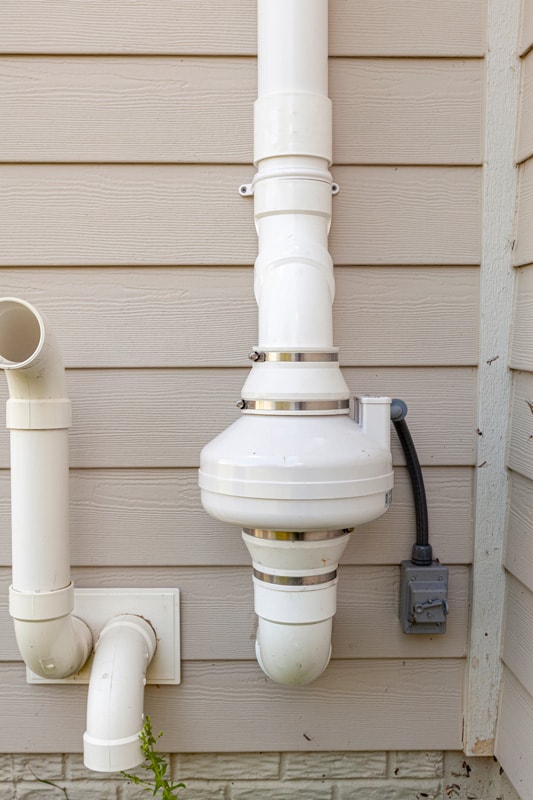

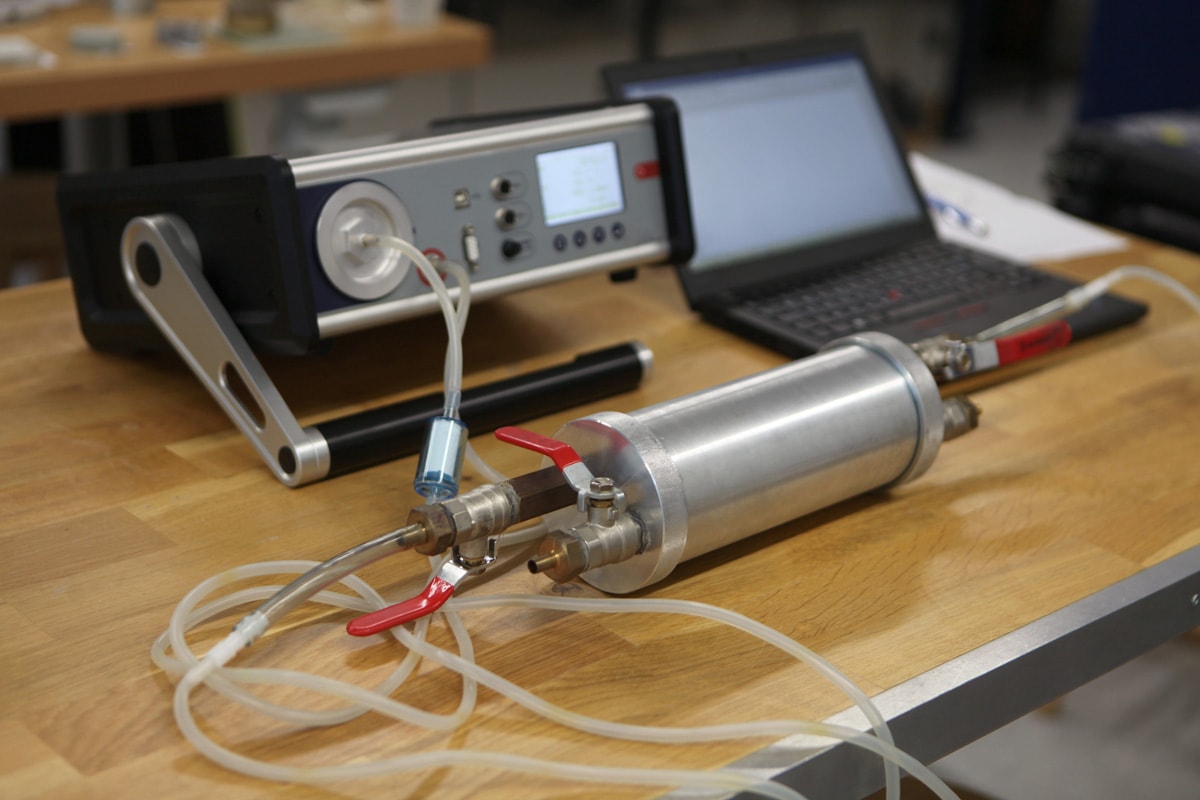
After sending the radon testing kit to a lab for the results, it would be best to take action for whatever the results are. Please refer to the following:
Four pCi/L Or More
The Environmental Protection Agency suggests a radon mitigation system if your residence registers four pCi/L or more.
One example is to have a professional install a sub-slab suction radon mitigation system. It is the most popular radon reduction technique, wherein you will need to have a pipe and fan installed to suck up radon from your house's foundation to discharge outdoors.
Less Than four pCi/L
If the results show that your house's radon level is less than four pCi/L, you should repeat the radon testing every two years. If you conduct structural modifications or move into a previously unoccupied level of your home., consider testing sooner or more often.
In addition, you should keep in mind that you can immediately install a radon mitigation system once it reaches two pCi/L. This is what most homeowners do since there is no particular radon level considered to be safe.
Related: "DIY Radon Mitigation Mistakes To Avoid [Read This First]!"
How To Reduce Radon Levels In Buildings?
If you plan to reside or build structures in an area where you think it is radon-prone, it would be best to know what to do to reduce its levels or concentrations. Good thing that the building codes of the US include preventative steps, and they are the following:
- Install a radon mitigation system.
- Improve the ventilation of the subfloor.
- Keep the basement door closed to prevent radon gas from seeping up from the basement into the rest of the house.
- Sealing the floors and walls and enhancing the ventilation system is essential.
- A common practice in homes with crawl spaces is to cover the floor with plastic.
- Substrate and domestic appliance testing
Please remember that installing a radon mitigation system is a must if you want to significantly reduce radon concentrations in your home or any structure.
Related: "What Is A Radon Mitigation System & How Does It Work? [Complete Guide For Homeowners]"
Wrapping It All Up
As a homeowner, you must be aware of everything happening to you and your house. Remember that one crucial factor always to consider and check is the radon concentrations in your home. It is a must since it can significantly affect your and your family's health, especially if ignored. It would be best to keep an eye on your basement and crawl spaces since you can most likely find high radon levels.
Made it to the end? We hope you find this post helpful. If you still have additional questions, please feel free to reach out in the comments, and we'll get back to you. Thanks for reading!