A lot of money is spent on regulating energy in the home and even industrial areas like hotels and offices. When using energy systems in the home, it is very crucial to understand their efficiency levels. You may want to know if PTAC is the same as a heat pump. You're on the right page because we have done our research and consulted HVAC experts to help us answer your question accurately.
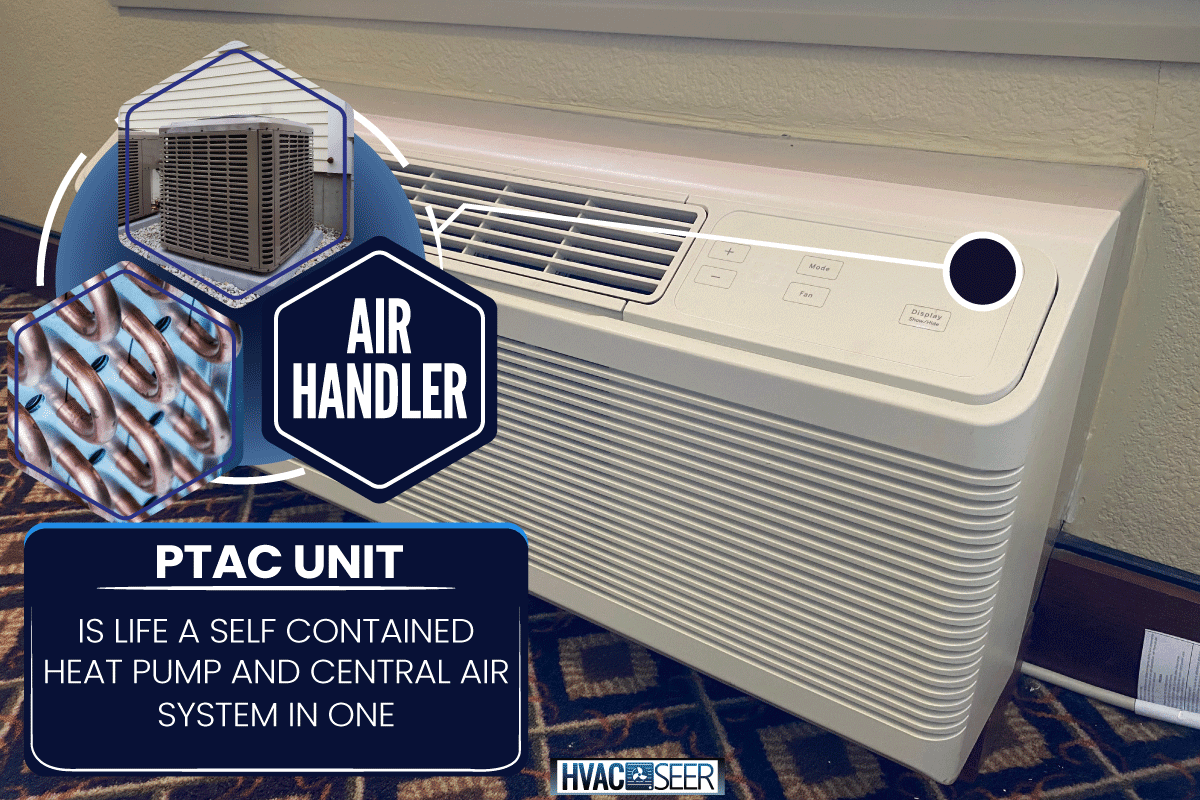
A PTAC unit is like a self-contained heat pump and central air system in one! The heat pump, evaporator coils, and air handler are all contained in a steel cabinet. Most PTAC units have built-in heat pumps.
PTACs with heat pumps are more expensive compared to those with just heat resistance. Keep reading to find out more about PTAC.
What Is PTAC?
PTAC stands for packaged terminal air conditioner. A PTAC is an independent air conditioner used to heat and cool small rooms. They are frequently spotted under the windows of numerous hotels and motels across the nation.
Hotels, hospitals, senior housing facilities, flats, and residential additions like sunrooms all employ PTACs to save expenses and improve energy efficiency. PTACs can be purchased with electric heating or with reverse cycle heating.
A PTAC is a self-contained unit, also known as a unitary heating and cooling system, meaning that all of its major parts, including the compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve, are housed and integrated into a single casing.

Is A PTAC A Heat Pump?

A PTAC unit is a reversible system that may be used for heating in the winter, cooling in the summer, and reliable temperature control that is made for all-year comfort.
When used for cooling, the refrigerant inside works to cool the coil, which helps with heat exhaustion and humidity removal. Heat and humidity are released via the unit's vent.
When used for heating, the refrigerant heats the coil in reverse, which is how it operates. Warm air is produced when air flows over this heated coil and is then released back into space. PTACs employ a heat pump or an electric heater for heating.
How Does A Heat Pump Work In A PTAC Unit?
PTACs use either fresh air intake or conventional refrigerant to chill the air. A condensing coil that faces the outside and an evaporator coil that faces the room being cooled are both used in PTACs.
Opening a window and using fresh air intake are similar actions. A vent in the back of the PTAC allows air to enter the system straight from the outside. Dehumidifiers that pull moisture from the outside air are also included in some versions.
However, the most popular and effective way is refrigerant-assisted internal air circulation. To cool the coil and remove the heat and humidity from the air, refrigerant is used.
The air is then let out of the appliance using fans and a valve. You can add a wall thermostat or use controls on the PTAC unit itself to regulate the temperature of the air in your home. A wall thermostat makes it possible to install a programmable controller with options for an energy management system or even Wi-Fi connectivity.
Resistive electric heat is present in every PTAC unit. That entails hot wires and a fan that blasts air across them, similar to a blow drier. A reverse cycle heat pump is also present in certain PTACs, but the majority simply employ resistive electric heat.
A heat pump operates in reverse but is otherwise similar to a window air conditioner. By adjusting the flow of the freon in the unit using a valve, it sends hot air into the building and cold air out the back. Compared to conventional electric heating systems, heat pumps use between 25 and 75 percent less energy.
What Is The Difference Between A Heat Pump And Heat Strip?
A heat strip component can be found in all heat pump systems. These strips, created using more conventional design principles, are coil-like components that produce heat when electricity passes through them. These strips transfer heat into your home by allowing air from your system to pass over them.
Compared to a heat pump, heat strips use a lot more energy. Because of this, these systems include heat strips for backup or emergency use. The amount of heat in the outside air may not be sufficient for your heat pump to function on its own if the outside temperature drops significantly.
In these circumstances, the system activates the heat strips, delivering any necessary extra heat so the heat pump can keep up.
A heat pump regulates heat from one place to another by using refrigerants. For an all-electric home in climates with below-freezing temperatures, a heat pump is typically more cost-effective and can be augmented with a heat strip kit.
The least effective heating alternative available to residences without access to a gas fuel source is heat strip kits, which are the only other choice.
It is crucial to keep in mind that heat strips use a lot more energy than heat pumps do. Because of this, depending on heat strips for any length of time can increase your electricity costs.
Do PTAC Units Bring In Free Air?
The lifespan of your PTAC may be negatively impacted by air recirculation. The unit will need to operate more vigorously in areas with external air recirculation, which will increase energy consumption and put additional wear on parts.
A PTAC unit works normally by drawing cool, fresh air into the outdoor side of the unit, which is then forced through the condensing coil.
When air passes through the condensing coil, the refrigerant inside the coil loses heat and returns to a liquid condition. The hot air is then released into the outside environment, where it mixes with the air to bring the temperature back down to normal.
When air is held in the wall sleeve rather than diffusing to the outer air, it is said to be circulating outside. As a result of the condensing coil using the trapped air again, the air temperatures rise even further.
Up to the point where the PTAC shuts itself off owing to excessive condensing temperatures or pressures or failing, the temperature of the air is constantly circulated through the condenser in this manner.
Are PTAC Units Energy Efficient?
The upfront cost of PTAC units with heat pumps is often higher than $50. Although you should anticipate saving money on your electric bills throughout the unit because they are far more energy-efficient, the higher initial cost will eventually be recouped.
When it comes to heating a space, heat pumps are less effective than electric heat PTACs. The energy efficiency ratio of the most effective PTACs in cooling mode is close to 12. Modern PTAC versions use a great deal less energy than outdated ones.
Do PTAC Units Have Thermostats?

Thermostats that are incorporated into PTACs are typical. An approach to temperature management that is considerably more practical is offered by a remote thermostat. With a remote thermostat, you or your visitors can control the temperature in a different area of the room—possibly one that is higher than the PTAC unit itself.
This prevents anyone from bending down to adjust the temperature, even if the PTAC is positioned at floor level. It is important to note that there is a need to put the wiring for the thermostat before the walls are closed up when installing a PTAC in a room that is still being built.
Also, You can get thermostats placed on the wall when installing a PTAC in a finished room. They are frequently accessible from the manufacturer. However, because of their difficult installation procedure, you can decide that it's only worthwhile if the room is still unfinished.
Will A Heat Pump Work Without Heat Strips?
Unless the outside temperature drops considerably below 40F, heat pumps do not require a heat strip. Heat pumps that are subsidized by utilities must have an outside thermostat fitted to prevent the heat strips from turning on unless the outside temperature is 40 degrees Fahrenheit or lower.
You only need them if your heat pump experiences a mechanical issue, such as a compressor failure or a refrigerant leak, as they will cost you a lot of money in electricity to keep the house warm while you wait for repairmen to arrive.
Do All Heat Pumps Have Auxiliary Heat?

Heat pumps provide some benefits, one of which is that they typically cost less to operate than furnaces. Installing a new system is still expensive; the cost to install a heat pump can range from a few thousand to more than ten thousand dollars.
However, heat pumps also have a built-in issue: Since they are unable to produce their heat, they are dependent on the presence of warm air outside to operate. When the air temperature falls below roughly 35 degrees Fahrenheit, an air-source heat pump won't function well.
To Wrap Up

A PTAC is a self-contained unit also referred to as a unitary heating and cooling system. For heating, PTACs use either a heat pump or an electric heater. For cooling, the refrigerant within works to chill the coil, assisting in the prevention of heat exhaustion and the elimination of humidity.
If you enjoyed this article, we recommend you read our similar posts about heat pumps