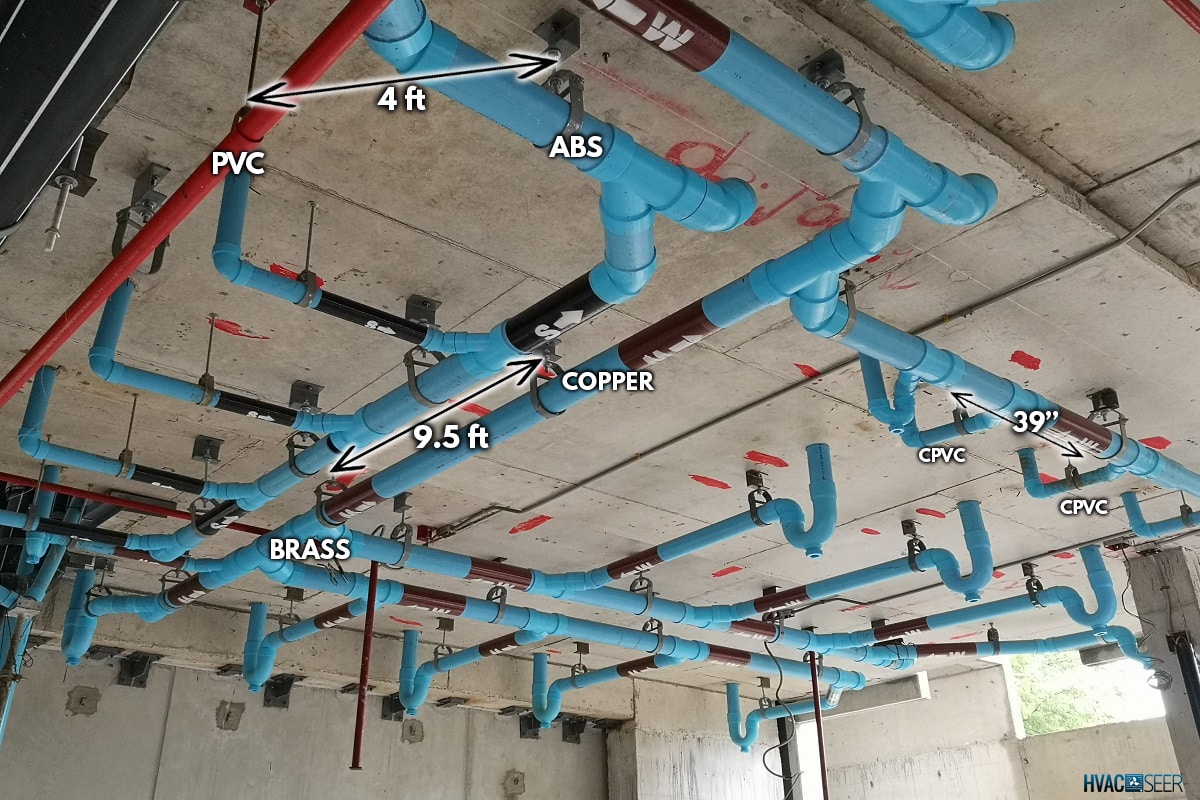
You are installing a piping system. You have come to a point where you need to install the support hangers and wish to know their exact spacing intervals along the pipes.
Are there any legal requirements relative to these hanger placements? We have done the legwork to give you the precise information you need.
The placement of pipe hangers should be code-compliant. It mainly depends on the type of pipe and its size.
Here are the standard pipes and the maximum horizontal spacing the hangers should be installed along the length of the pipe.
- ABS and PVC 4 feet
- PEX 32 inches
- copper and brass ( >1" size) 9.5 feet
- copper and brass ( <1" size) 8 feet
- CPVC 39 inches
- cast iron 9.5 feet
- steel and galvanized 8 feet
Pipe hangers are one of the significant components of any piping assembly. This post will discuss the critical information you need to know to determine their spacing and correct placement within the system.
Stay on this page as we discuss this further.
The Piping System

Nobody can overlook piping systems. You could see pipes interconnecting with each other in both residential and industrial settings.
While pipes for residential use are usually plumbing, heating, and ventilation systems, they are simpler in structure than industrial setups.
Pipes in industrial settings are more complex and span a larger area. In one structure, you could see numerous types of pipes in varied sizes. Pipes convey liquids, gasses, slurries, powders, and small solids.
Along the interlocking pipes are its components, such as the fittings and, of course, the hangers.
Pipe hangers form the support system of the piping system. Due to its crucial role, the IPC (International Piping Code) has set the requirements for its correct placement, spacing, and intervals.
If you wish to learn more about piping design and layout, these posts are worth reading:
Can I Bond Gas and Water Pipes Together? and Water Pipe and Electrical Cable in Same Trench? Is it Safe? Here's What You Need to Know
What Are Pipe Hangers?
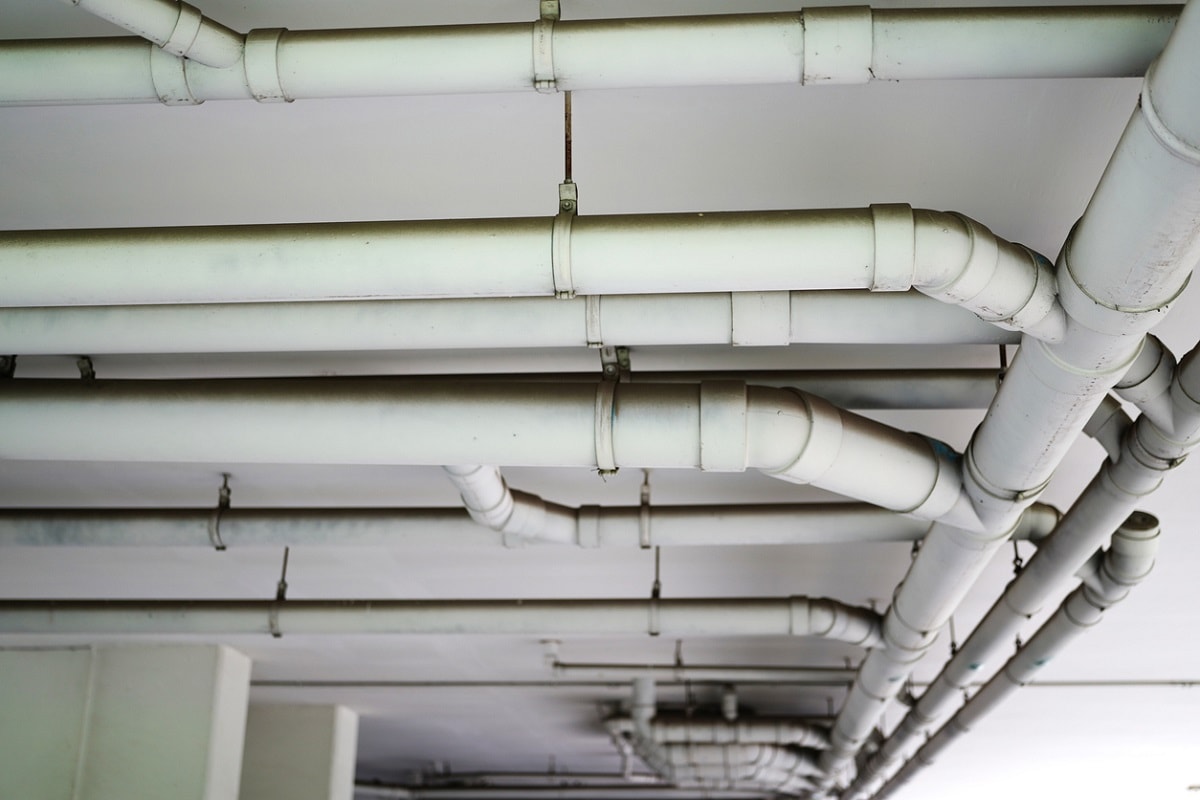

Pipe hangers can take many forms as support devices for pipes. They come in brackets, clips, clamps, and loops to suspend pipes from ceilings and overhead beams.
These hangers transfer the load from the pipe to the supporting structures.
The load may come from the pipe's material weight, the contents it transports, the attached fittings such as tees and flanges, and any coverings such as insulation.

To achieve the hangers' design to lessen or distribute the load of the pipe, the proper spacing interval should be maintained.
The Spacing of Pipe Hangers

The IPC governs the placement or intervals of pipe hangers. It primarily depends on the type of material used in the pipe and its size or diameter. Here are the standard pipes and the maximum spacing between hangers.
ABS and PVC
For ABS and PVC pipes, regardless of diameter, observe at least 4 feet intervals of the hangers.
Commonly used for plumbing systems, these pipes have plastic and resin components. These durable materials resist water degradation, higher shock, and impact.
PEX
PEX pipes are made of flexible plastic, and their diameter ranges from 3/8 to 1 inch. Since it is made of a lighter material and smaller pipe sizes, a 32" maximum requirement for hanger spacing is adequate.
CPVC
CPVC pipe is a cousin of PVC. What differs is that it contains thermoplastic material, which makes it perfect for hot water applications. It withstands temperatures up to 200 degrees Fahrenheit.
Due to this high resistance, the maximum hanger spacing is 39" or 1 meter, regardless of diameter.
Copper
Copper pipes are standard in industrial settings due to their dependability and are highly anti-corrosive. It is perfect for water, drain, and vent lines for residential use.
The material is made of rigid copper with superior strength to withstand stresses. Due to this, a high maximum limit of hanger spacing of 9.5 feet is allowed.
Copper tubings are primarily used in HVAC systems. It is more expensive with lighter tolerances and a smaller pipe size of 1" and less, which is best for refrigerant lines.
Due to its size but with the same material as copper pipes, 8 feet is the maximum hanger spacing interval.
Brass
Brass pipes are less durable but more resistant to corrosion than copper. They contain zinc that makes them stronger and ductile, perfect for plumbing and mechanical components.
Like metal, brass has a maximum hanger spacing of 9.5 feet for pipes and 8 feet for tubings.
Cast Iron
A cast iron pipe gives a water-tight seal that withstands heavy ground movements. It is a high-pressure pipe perfect for water, gas, and sewage transmission.
Due to cast iron's superior compressive strength and very dense material to withstand heavy loads, a maximum of 9.5 feet for hanger spacing is sufficient.
Steel
Steel pipes have gradually replaced cast iron in the construction industry over time. As corrosion is the major drawback of cast iron, steel has proven its superior strength against loads and significant stresses.
The IPC code has maintained the 8 feet hanger spacing interval for standard steel pipes.
The above data are for horizontal piping, and the hangers are positioned along the length of the pipe. Vertical pipes are supported at the base with a 7.5 meters maximum interval of hangers.
Other Factors To Consider In The Placement of Pipe Hangers

Piping systems are complex. The data presented above serve as a guideline.
Pipe material and size are only the basics in determining the spacing of support hangers. However, there are still other equally important factors to consider.
The Magnitude of the Weight Load
Since pipes convey liquid, gas, and small solids, the weight of the contents isn't evenly distributed along the length of the pipe.
There are specific spots where the weight load is concentrated. As such, additional hanger supports are added to these areas.
Also, in areas where pipes bend or change direction, there is a concentrated weight load. As such, it is an industry practice to install hangers within two feet on both sides of the pipe joint.
Changes in direction are supported to reduce the tension stress of pipes.
Pipe components, such as valves, flanges, and tees, should be independently supported since stress is concentrated in these areas.
For example, valves should be adequately supported to prevent unnecessary movements due to torque pressure.
For pipes that carry small solids, there are areas where the contents tend to accumulate. As such, additional hangers are needed to support these areas.
The Operating Temperatures
Temperature affects the tensile strength and compressive strength of the piping material. When the pipes operate at high temperatures, additional hanger supports are needed.
Providing continuous support through hangers is also recommended when pipes operate near the maximum temperature limits.
Other Pointers for Pipe Hangers
Hangers for copper and brass pipes should be of the same material to protect them from corrosion. For example, a steel hanger will rust if used on a copper pipe.
Pipes with their surrounding equipment should be supported independently. For example, a pipe should not be hung from another pipe. Also, a nearby tank should be supported separately from the adjacent piping.
Why Pipe Hangers Are Needed?
Hangers should be capable of securing the pipe and its contents from unwanted movements and displacement, including vibrations.
The hanger support should anchor and play as a shock absorber from the pipes' load stress.
Without the proper support, the following could happen, not only to the pipes but to the whole piping assembly and infrastructure.
Stress Build-Up
Pipes endure stress at specific points along their line. There is stress where weight is concentrated and at bending points. Installing supports in these areas helps reduce stress by distributing the weight towards a wider portion of the pipe.
Pipe Sagging
This commonly happens in ABS and PVC pipes. Sagging displaces the positioning of the pipes.
Heat and load weight are the causes of pipes sagging. If this problem is not addressed promptly, blockages in the flow and improper venting will occur.
Mechanical Failure
The absence of pipe support causes undue strain on the joints and may lead to breakages.
Pipe breakage damages not only the pipes but the whole system. At its worst, it may cause catastrophic damage to your property or infrastructure.
Thrust
Like any mechanism, the serviceability life of the pipe is shortened when it continually operates under undue stress.
Additionally, you could also hear unwanted noise due to vibration. Pipe hangers can help avert these strains on the pipes.
Maintain the design layout and slope
Since hangers are designed to contain the pipes from undue movements, the design layout of the whole piping assembly can be maintained, including the slope.
With adequate support hangers, even with the presence of weight load stresses, the positioning of the pipes can stay at their original design layout.
Expansion
Pipes expand and contract due to temperature changes and pressure fluctuations. The hangers can help support the pipe due to thermal factors.
Insulation materials may be added to help cushion the pipes from extreme temperatures.
You might be interested to read more about adding insulation to pipes; read these posts:
How to Insulate Swimming Pool Pipes and How to Insulate a Main Water Line Pipe
To Sum It Up
Pipe hangers play a crucial role in providing support to every piping system. Proper spacing intervals, as set by the IPC, should be maintained to achieve this.
As a rule of thumb, pipes of lighter materials, such as plastic and resin, have the least hanger spacing interval ranging from 32 inches to 4 feet. These are the ABS, PVC, PEX, and CPVC.
Pipes made of heavier metals such as copper, brass, cast iron, and steel range from 8 to 9.5 feet.
The smaller the pipe sizes and the lighter the weight load, the nearer the hanger spacing. As pipe sizes increase, the hanger spacing interval also increases. Water pipes carry less load than gas pipes.